Leveraging a Temperature Converter Across Food Manufacturing, HVAC System, and Laboratory Settings
A temperature converter is a powerful tool that helps convert various temperature units instantly. From Fahrenheit to Celsius, Celsius to Fahrenheit, or Celsius to Kelvin, and many other cross-conversions are performed quickly and easily through a temperature converter.
So, what are the reasons for doing these conversions? The answer is simple. In business industries, several requirements need accurate temperature measurements. Thus, the businesses leverage the tool to identify various temperature values.
Food manufacturing, HVAC systems, and laboratories are some examples that require accurate temperature conversions. So, the tool is a must-have assistant to perform work-related tasks perfectly.
Key Takeaways
- Understand what is a Temperature Converter Tool.
- Identify various temperature units and conversion examples.
- Identify the Temperature Converter applications in different business areas.
What is a Temperature Converter Tool?
A Temperature Converter is an online tool that helps convert different temperature units. Smart Tools AI offers a simple yet powerful tool that can convert values between Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, and Rankine.
The tool is easy to use without any complicated technical jargon. Whatever the conversion needs you have, just select the units from the dedicated selection boxes and the conversion amount will be displayed on the top within a second.
For example, if you need to convert from Celsius to Kelvin, select both units from the suitable boxes and apply the required numbers. For instance, if you add 50 Celsius the converter displays the amount as 323.15 Kelvins.
01. Temperature Converter in Food Manufacturing
Food manufacturing companies rely on temperature measurements for various reasons. But the most essential reasons are ensuring food safety and quality, and monitoring the food production processes. Let’s check one by one:
A. Ensuring Food Safety and Quality
Providing good foods and beverages is a necessary responsibility of the manufacturing companies. While involved in the production process, there can be chances for micro-organisms or bacterial growth which can contaminate the food condition. Here, the temperature measurements play a pivotal role in ensuring food safety and quality.
For example: A tuna processing facility must adhere to the standard temperature rate throughout the production process. Cooking tuna in the oven, storing it in the coolers, and post-market storing involve setting and adhering to standard temperature measures to ensure the safety and preservation of tuna foods. Let’s break this down for different kinds of food items in different temperature units.
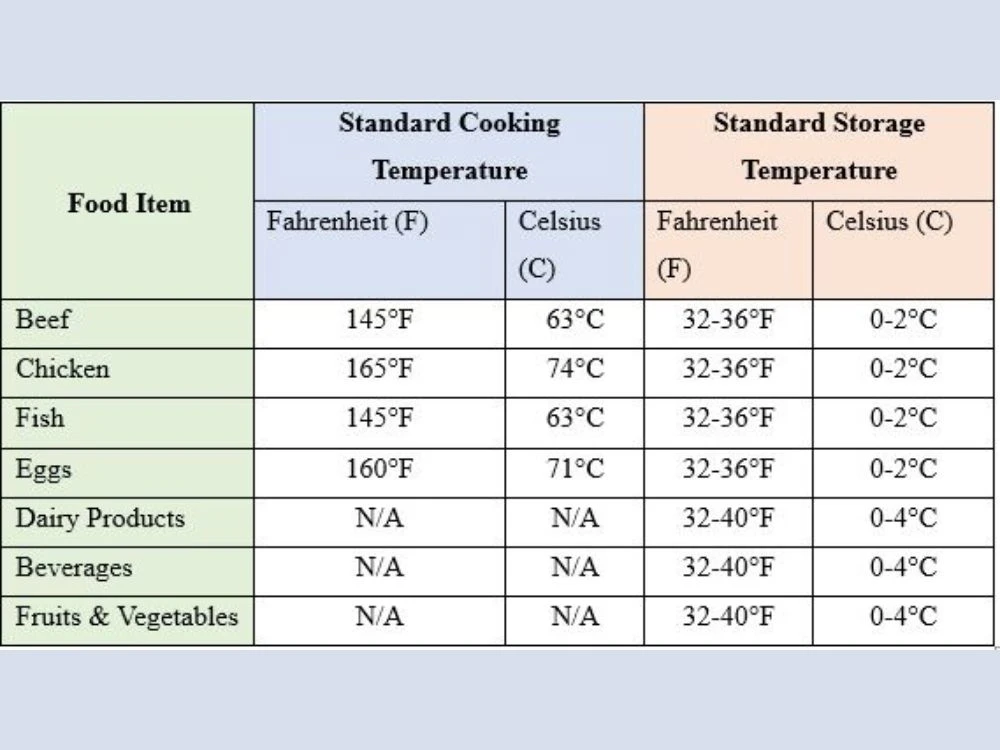
This table displays the standard temperature for cooking and storing foods to avoid bacterial development and food contamination. The companies must comply with relevant food safety regulations and their standard temperature level. This way the food will remain safe to the end users or consumers.
B. Monitoring Production Processes
Another crucial reason for using a temperature converter in the food manufacturing sector is to monitor food production processes to effectively produce food items consistently.
For example: A bakery requires precise temperature control for getting desired product characteristics such as texture and color. The Temperature Converter helps enable bakeries to correctly adjust their oven temperatures and specific baking times. This is important to produce consistent, high-quality products.
Likewise, in beverage manufacturing, maintaining the correct temperatures during fermentation and pasteurization processes is vital to ensure product integrity and shelf stability. See the table below for an easy identification:
| Food Production Process | Temperature Requirement |
| Baking (bakery) | Oven temperature: 325-450°F (163-232°C) Baking time: Varies based on recipe. |
| Fermentation (Beverage) | Temperature varies based on beverage type and yeast strain used (typically 65-75°F or 18-24°C for beer fermentation) |
| Pasteurization (Beverage) | Typically, 145-165°F (63-74°C) for the pasteurization process. |
| Canning (Food preservation) | Sterilization temperature: Typically, 240-250°F (116-121°C) for low-acid foods, and 212°F (100°C) for high-acid foods. |
| Chocolate Tempering | Tempering temperature: Varies based on chocolate type, typically between 86-90°F (30-32°C) for dark chocolate, and 82-86°F (28-30°C) for milk chocolate. |
Remember, this temperature standard may vary based on local food safety regulations. Mostly a slight variation is there but this table may give you an overall idea about keeping the temperature level while producing food items.
02. Temperature Converter in HVAC System
A. Precision Control for Comfort
An HVAC (Heating Ventilation & Air-Conditioning) system is directly responsible for maintaining the indoor air quality of a business. Since an HVAC system fulfills heating or cooling (mostly cooling) requirements, it must produce a standard temperature.
The system ensures internal comfort where occupants feel less fatigued. This has a direct connection with employees’ productivity enhancement. A global standard is maintaining 20 - 25 degrees Celsius or 68 - 77 degrees Fahrenheit to maintain internal comfort.
To precisely control the temperature in the building, an HVAC system requires a temperature converter to generate certain set points in the system.
B. Energy Efficiency Optimization
Another prominent aspect of the HVAC system is energy efficiency optimization. Maintaining the correct temperature will help optimize energy and save some money for the business. Let’s see how:
The HVAC system is designed based on the cooling load requirements. The floor area and heating emissions from people and equipment are taken into consideration to calculate the cooling load requirement. This will help choose the right capacity HVAC system.
Also, the temperature converter assists in finding different temperature units that help set and adjust indoor temperatures. A BMS system is also efficient in doing this where it automates everything to match the temperature level in the building. This is crucial to save energy where thermostats are effective in identifying the room temperature and adjusting actuators to control airflow based on the room surface requirements.
Additionally, it is important to conduct energy-saving programs to guide employees. Training may help them understand different temperature units, setting the machinery and components for specific requirements, and other energy-saving tips at the occupiers’ and maintenance workers’ level.
03. Temperature Converter in Laboratory Settings

A. Supporting Research and Development
Temperature Converter plays an important role in laboratories. Scientists, chemists, medical researchers, and research students who work in laboratory settings require accurate temperature data for conducting research and development.
The research can be related to biology, chemistry, physics, or any other scientific subject matter. Using a Temperature Converter tool helps perform the experiments accurately. The tool assists the professionals adjust the temperature settings on various laboratory equipment.
For example: When studying the superconductors’ properties, researchers work with extremely low temperatures approaching absolute zero. It is defined as 0 Kelvin (-273.15°C). Temperature Converters facilitate communication and data exchange between different temperature scales and allow researchers to convert temperature readings from Kelvin to Celsius or Fahrenheit easily.
B. Ensuring Accuracy in Experimentation
Ensuring accuracy is a critical aspect in laboratory settings where a slight mistake can also lead to significant problems. When conducting experiments, professionals need to keep experimental stuff at standard temperature levels.
For example: Medical laboratory technologists (MLTs) are required to perform medical diagnostic tests where they should follow specific temperature settings to get accurate test results.
Likewise, materials science experiments require accurate temperature control to understand phase transitions, thermal properties, and crystallization processes. Temperature Converters help researchers to convert different temperature readings between different scales, such as Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. This will assist in ensuring consistency and accuracy in experimental measurements.
Wrapping Up
A Temperature Converter is a useful tool to convert different temperature units. Various industries like food manufacturing, HVAC, and laboratory settings require precise temperature conversion results to perform certain tasks.
By using the tool, the food manufacturing sectors can ensure food safety and produce consistent quality food and beverage items. Similarly, in HVAC systems, the tool helps ensure internal comfort through precision temperature control and also ensures energy efficiency.
Moreover, medical laboratory, and scientific research professionals utilize the Temperature Converter for supporting research and development works and to get accurate experimental data.
FAQ
Q1: What is a Temperature Converter tool?
A tool that assists in converting different temperature scales like Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, and Rankine accurately and quickly.
Q2: What are some other applications of a Temperature Converter tool apart from the discussed areas in the article?
The tool can be useful for various industrial settings other than the discussed things in the article. It is useful for meteorologists, pharmaceutical industries, construction industries, and many more.
Q3: What is the standard temperature for internal building comfort?
The global standard is 20-25°C which equals 68-77°F. Below this temperature can make a person shiver and above this temperature can make the person swelter. So, keeping the temperature in between the standard can be ideal.
Q4: What is Rankine and how much is the Kelvin value of one Rankine?
Rankine is one of the temperature scales that is mostly used in the United States for engineering applications. One Rankine equals 0.56 Kelvins.
Explore Related Posts
https://smarttoolsai.com/post/food-and-beverage-industry-and-electric-unit-converters
.webp)