
Torque Converter: Understand It and Ensure Automotive Industry Efficiency
A torque converter is a significant component in the automotive industry and it is used in automatic transmission vehicles. This component is commonly placed between the engine and the transmission system. The main functionality of the torque converter is to ensure sufficient power flow that enables the vehicle to move efficiently.
On the other hand, in manual transmission vehicles, there is a clutch system to ensure the function of a torque converter. For instance, imagine a scenario where you halt at a traffic light in a manual transmission vehicle. To smoothly resume movement right after the stop, you must engage the clutch pedal and release it. It will ensure a good transfer of power.
Now, if you think about the automatic transmission vehicles they don’t have a clutch system. So, how can you ensure the power flow (acceleration) during stops or idle moments? This is where you must understand the importance of a torque converter that helps ensure efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Understand what a torque converter is, its components, and its operational mechanism with examples.
- Learn different types of torque measurements and the utilization of an online torque converter tool.
- Understand the impact of a torque converter on the automotive industry efficiency.
What is a Torque Converter?
A torque converter is simply identified as an important component used in automatic vehicles to ensure smooth movement. The primary purpose of this component is to transfer adequate power (torque) from the engine to the transmission, the drive shaft, and the drive wheels of a vehicle.
In addition to that, the torque converter ensures that the speed and torque of the drive wheels sync well with the engine’s speed of the vehicle. Plus, to shift gears and to come to a stop, you must use clutch pedals in manual transmission vehicles, but in automatic vehicles, there is no clutch which requires a torque converter to perform the clutch functions.
Confused? Let’s make this clear. In manual transmission vehicles, you pedal the clutch to shift gears and to come to a stop which helps disconnect the constantly spinning engine and drive shaft. But what happens if there is no clutch to interrupt the connection between the drive shaft and the vehicle’s engine which is common in the automatic transmission vehicle?
Here, if you try to stop the drive wheels and there is no clutch or torque converter in place, the engine dies. So, automatic transmission vehicles should have a torque converter to properly disconnect the engine shaft from the drive shaft when shifting gears and stopping the vehicle.
Additionally, the torque converter provides enough power and torque to the vehicle for a smooth and good pickup in automatic vehicles. Now you may understand what a torque converter is and its importance. Let’s discuss how this component works in the next section.
How Does a Torque Converter Work?
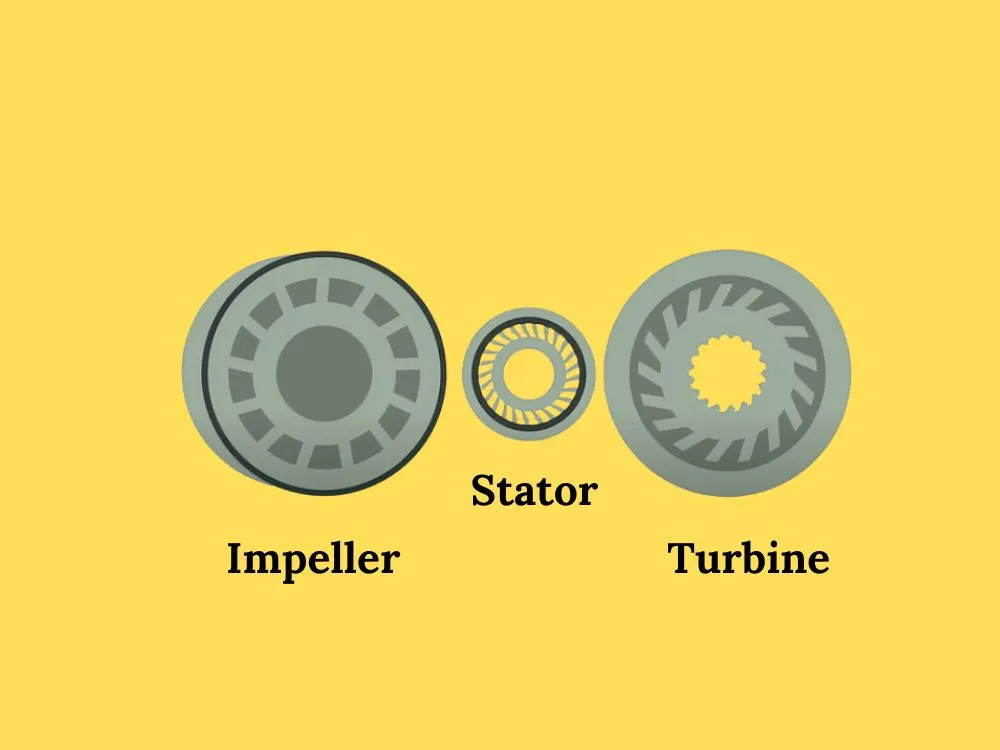
Before getting into the operational mechanism of a torque converter, it is crucial to understand the vital components. The torque converter has 3 major components such as the impeller, turbine, and stator. The torque converter housing is generally bolted with the engine’s flywheel (See the diagram below). Thus, it turns at whatever speed the engine turns.
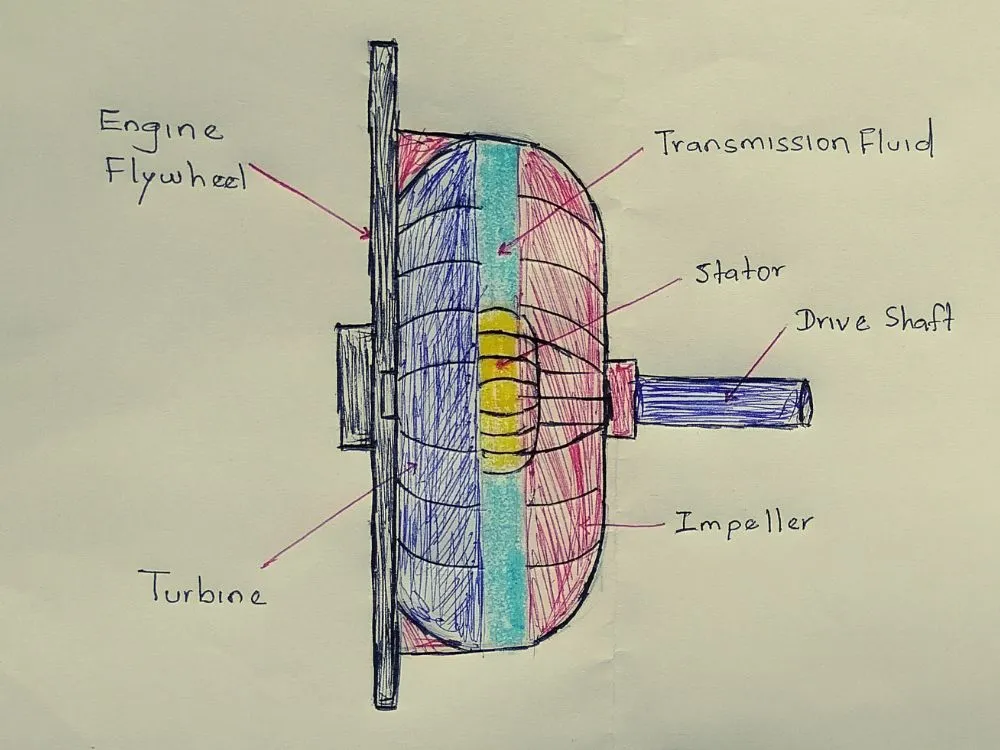
Impeller or Pump:
The impeller has fins all over it and is welded inside the torque converter housing. Here, the impeller spins with the engine and while it’s spinning there’s transmission fluids get in here which are caught by the impeller fins and thrown outward.
The impeller is also a type of centrifugal pump where it flings out the liquid when the fins spin. It’s similar to a blender where you find a small blade spins at the bottom. This blade in the blender spins so fast that it is capable of shooting the liquid all the way to the side and out. This is called the centrifugal force.
Now imagine that you put the blender horizontally and all things spin, that’s how the fins in the torque converter work. Also, the impeller is primarily connected to the engine’s crankshaft and it works by harnessing the engine’s rotational energy.
Turbine
The turbine is another primary component of the torque converter. This is connected to the transmission shaft of the vehicle and is responsible for powering the transmission and drive wheels. It operates by harnessing the flow of transmission fluid initiated by the impeller.
In simple terms, you know that the impeller propels transmission fluid towards the turbine. This fluid flows onto the turbine blades and causes the turbine to spin. This spinning action helps convert the kinetic energy of the flowing transmission fluid into mechanical energy. The converted mechanical energy is then utilized to propel the vehicle forward.
Also, the turbine in the torque converter is loosely mounted because it has to be driven by the force of transmission fluids sent by the impeller. To make the operational mechanism even more clear, see this example:
Imagine that you’ve got two fans where one is powered by electricity (like the impeller) and the other one sits opposite it (like the turbine). Here, the second fan that doesn’t use electricity can spin with the airflow generated by the first fan that uses electricity.
Similarly, in a torque converter, the impeller (powered by the engine) initiates fluid flow which makes the turbine spin and transfer energy to the transmission. Just like the stationary fan spinning due to the airflow from the powered fan.
Stator
The stator in a torque converter plays a crucial role in optimizing torque transfer and minimizing churning loss within the fluid coupling mechanism. Generally, the component sits between the impeller and the turbine (see the image below).
The stator also ensures efficient energy transmission. Plus, it strategically redirects the fluid which helps enhance the fluid coupling's effectiveness and reduce churning loss associated with turbulent fluid movement. This optimized flow contributes to smoother operation and improved overall performance of the torque converter in automatic transmissions.
Just see this example to comprehend this thing even more clearly. If you imagine the transmission fluid flowing out of the impeller like water from a garden hose. Now, think that the stator is like your thumb placed at the edge of the hose.
Just as your thumb increases water pressure by restricting flow, the stator, with its fixed sharp blades can enhance torque and efficiency by directing fluid flow in one direction. This directed flow boosts the speed of the turbine and improves the overall performance of the torque converter.
Now you understand the operational mechanism of a torque converter and how all important components work together. The following chart can explain the discussed operation in a summary:
- Engine Running — Impeller Spins — Transmission Fluid Flow
- Transmission Fluid Flow — Turbine Spins — Power to Transmission
- Transmission Fluid Flow — Stator Redirects Flow
- Power Transferred to Transmission — Vehicle Moves
Understand Torque Measurements and Online Torque Converter Tools
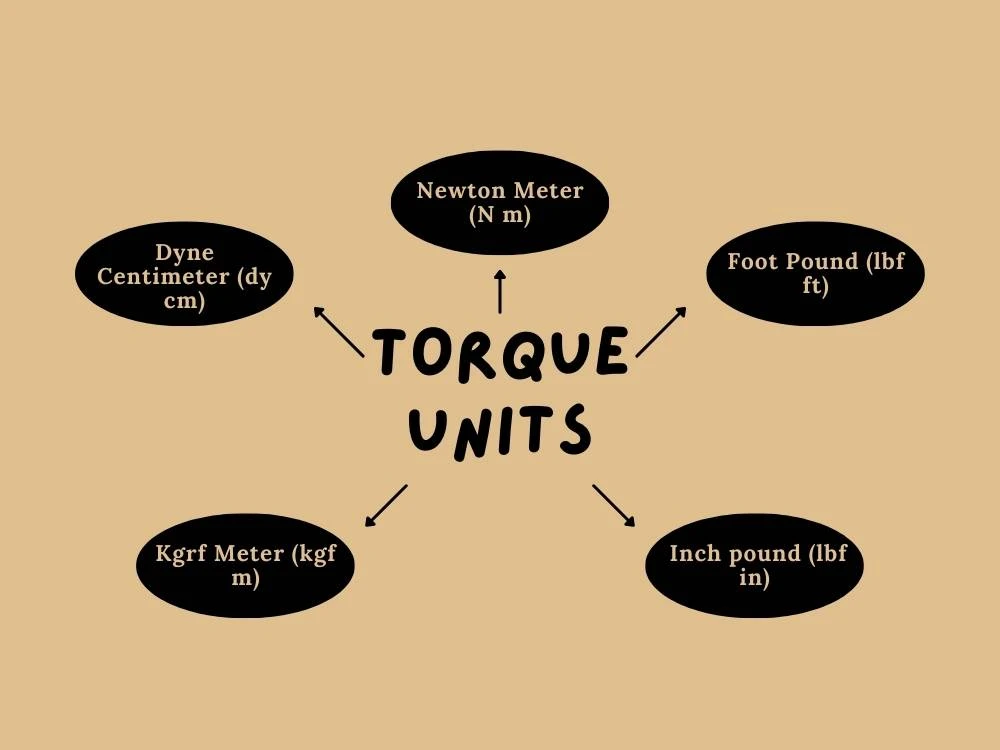
A. Various Torque Measurements
Torque is like the twisting force that is used to turn bolts with a wrench. It is crucial in various tasks, especially in the automotive industry. Torque plays a significant role from tightening screws to powering big machines.
In the automotive sector, torque converters and their components, like the impeller and turbine, rely on torque measurements to ensure smooth movement and power transfer in automatic vehicles.
Now you understand the importance of measuring torque. Let’s see some common ways to measure the torque:
- Newton Meter (N m): This is the standard measurement for torque and is essential for assessing power and performance in automotive systems like engines and transmissions.
- Dyne Centimeter (dy cm): This unit measures tiny twists, akin to using a small screwdriver on a small screw, which is essential for precise adjustments in automotive components.
- kilograms-force per meter (kgrf m): When working with heavy machinery such as engines or large vehicle parts, we need a lot of twisting force, which we measure in kilograms-force per meter (kgrf meter). This substantial torque is essential to make sure these heavy components operate efficiently.
- Foot Pounds (lbf ft): In the automotive sector, torque measured in pounds and feet is crucial for tasks like tightening bolts and securing various components.
- Inch Pounds (lbf in): This is similar to foot pounds but measured in inches. It is often used for precise torque specifications in automotive assembly and maintenance.
Understanding these torque measurements is vital for automotive engineers and technicians to ensure the proper functioning of vehicle components and systems.
B. What is an Online Torque Converter Tool?
An online torque converter tool, such as the one available at Smart Tools AI, is a convenient tool used to swiftly and accurately convert different torque measurements. It's not the physical component discussed earlier but it's a digital resource that is accessible through the internet.
With this tool, users can easily convert torque measurements between various units. Also, it makes calculations simpler and faster. For example, if you want to convert Newton meters to inch pounds, just go to the tool’s page and select both units in the designated sections. Now enter any random desired numbers and the tool will bring you the conversion result. For example:
You enter 10 newton meters and want the conversion in inch pounds which brings you the result as 88.5075. Plus, this online torque converter tool is important because it simplifies the process of converting torque measurements which saves time and ensures accuracy.
This helps technicians, engineers, and enthusiasts in the automotive industry, as well as in various other fields where torque is a critical factor.
Impact of a Torque Converter in the Automotive Industry Efficiency

The impact of a torque converter on the automotive industry efficiency is huge. It plays a significant role in the following ways:
Fuel Efficiency: A torque converter is helpful for automatic cars to use fuel more efficiently. Also, the component ensures the engine runs smoothly which helps prevent fuel waste, especially during cruising. Nowadays, the torque converters come up with special features such as lock-up clutches which help save even more fuel when you are driving at a steady speed.
Vehicle Performance: Torque converters make vehicles perform better. They provide adequate torque to the vehicle which allows it to accelerate smoothly. More torque means more power. Just think of it like a smooth and powerful push every time you step on the gas pedal.
Maintenance Costs: When torque converters work well, they help keep maintenance costs lower. The component is useful to protect the transmission and other essential parts from wearing out too quickly. But if you encounter any problems with the torque converter, it can be expensive to fix. So, you must take care of it by frequently checking fluids and getting regular check-ups.
Conclusion
In the automotive industry, the torque converter is super important. It makes sure power moves smoothly from the engine to the wheels. This helps cars use fuel better, perform well, and keep maintenance costs down.
Plus, with the help of torque measurements and online torque converter tools, it's easier than ever to understand and work with torque in vehicles. As technology gets better, the torque converter keeps improving to make driving easier and more efficient.
FAQ
Q1: What is torque in a vehicle?
A1: Torque is simply identified as the measurement of power a vehicle can produce. It means the more torque a vehicle produces the more the power and acceleration.
Q2: Which type of vehicle has a torque converter?
A2: Only automatic transmission vehicles do come up with this component while manual transmission vehicles use clutch to do the function.
Q3: What is an online torque converter tool and how does it help?
A3: The online torque converter is a digital tool that helps convert different torque measurements accurately. The measuring units used to measure torque are Newton meters, dyne centimeters, kilogram-force per meter, foot pounds, and inch pounds.
.webp)