
Exploring Waste Management and Thriving Careers in the Industry
Have you ever thought about what happens to your trash after you toss it away? Do you think it’s simply thrown into the land or buried? In reality, waste is properly managed through a sequence of steps.
Imagine a day without waste management. Trash piling up, streets overflowing, and health risks skyrocketing. This is why proper waste management is important.
What is Waste Management?
Waste management is the systematic process of effectively managing waste from its generation point (origin) to the final disposal. The goal is to manage waste safely and responsibly to minimize its negative impact on health and the environment. Effective waste management follows these key steps:

- Waste Collection: Gathering waste from different areas or sources.
- Sorting: Separating waste into relevant categories such as recyclable, biodegradable, or hazardous. This helps streamline further treatment.
- Storing: Temporarily keeping waste in appropriate containers or facilities. This is vital to prevent contamination and ensure safety.
- Transporting: Properly moving waste to treatment plants or disposal sites using suitable vehicles.
- Treating or Disposing: Processing waste through appropriate methods like recycling, composting, incineration, etc. This helps reduce the environmental footprint.
While handling waste in an organization, employees and other occupants may have several chances to be exposed. Therefore, the organization should pay adequate attention to safely disposing of the waste without impacting the internal parties. Plus, the main intent of waste management is to mitigate adverse health and environmental impacts.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the concept and significance of waste management and explore related career opportunities.
- Learn the steps involved in waste management, such as collection & sorting, storage, transportation, treatment, and disposal.
- Identify different types of waste (solid, hazardous, organic) and their handling requirements.
- Explore different waste treatment and disposal methods such as landfilling, composting, recycling, inertization, incineration, chemical disinfection, and gasification.
- Discover new technologies like smart bins and AI sorting that enhance waste management efficiency.
Importance of Effective Waste Management
Effective waste management is crucial as it helps mitigate issues such as waste-related diseases, bad odors, injuries, environmental impacts, and profit losses. Without proper practices, organizations may face these problems.
Understanding waste management at all levels of an organization is essential as it brings numerous benefits like enhancing employee productivity, aiding in achieving business objectives. and improving workplace conditions.
Waste Management Careers
These careers provide various opportunities for individuals who are passionate about people's health and environmental sustainability. They are classified under different groups, such as:
- Waste Collection and Disposal: Garbage Truck Driver, Waste Collection Crew
- Waste Treatment and Recycling: Recycling Specialist, Waste Treatment Plant Operator
- Environmental Compliance and Regulation: Environmental Consultant, Waste Management Analyst
To explore these careers quickly, just scroll to Section 4: "Career Opportunities in Waste Management."
Understanding Waste Management in Detail

Types of Waste
Several types of waste could be generated in an organization. So, it needs efficient handling and disposal. Here are some common types of waste:
- Solid Waste: All kinds of solid and tangible waste materials such as discarded papers, plastics, cardboard, metals, furniture, and others. It needs huge storage space until disposal and needs proper handling to avoid exposure.
- Hazardous Waste: These types of waste can cause severe harm to people and the environment because they contain hazardous elements. Common examples of hazardous waste are sharp materials, chemicals, electronic residues, expired pharmaceuticals, and so on. Generally, hazardous waste is harmful to human beings and causes injuries or diseases. This issue can be mitigated through effective waste management techniques.
- Organic Waste: This is biodegradable waste that originates from plants, animals, and other natural sources. Some common examples of organic waste are known as food scraps, fruits, and vegetable peels.
The Waste Management Process
The process involves a sequence of steps that support to effective disposal of waste from the organizational premises. Here are the steps below:
- Collection and Sorting: Waste collection is an important step in the waste management process, where a company must allocate adequate resources. Every day, waste is generated in huge quantities, and it should be appropriately collected. Properly sorting them (segregating) into proper categories, such as paper, plastic, organic, and hazardous types, is important. Sorting helps in segregating waste into the right categories, which is important for choosing the best treatment options later.
- Storage: After collecting the waste, it remains on the premises for a certain period before disposal. Proper storage methods and designated areas should be arranged to safeguard people from obstructions and health issues. Generally, organizations allocate a common storage area for waste. Use our area converter tool to determine the appropriate storage space needed for your waste management needs.
- Transportation: It involves transferring waste from its point of origin to a designated disposal area. Proper equipment and vehicles must be used to avoid dangerous exposures. This includes utilizing appropriate machinery to lift heavy waste loads and selecting high-quality vehicles that are suitable for the task.
- Treatment and Disposal: At this stage, waste is either disposed of or treated using methods such as landfilling, incineration, recycling, reusing, composting, inertization, gasification, waste autoclave, and more. These treatment methods can be beneficial in converting waste into useful products.
Waste Treatment and Disposal Methods
It's important to follow proper waste treatment and disposal methods to manage waste effectively. It helps reduce human and environmental impacts. Let's see some proper methods for waste treatment and disposal:
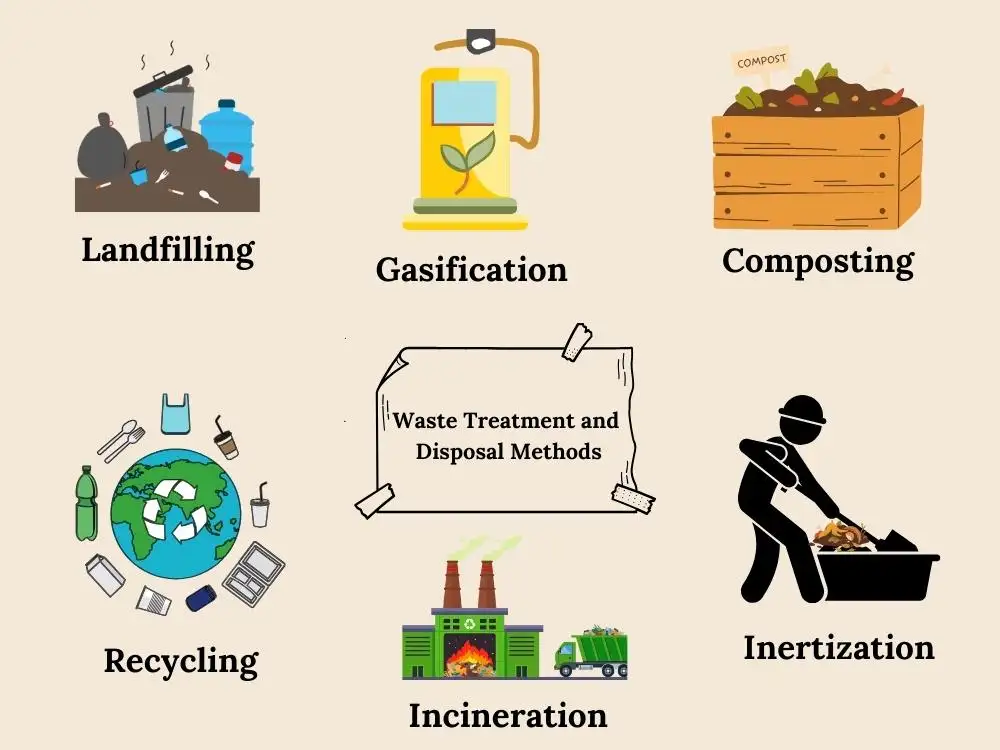
- Landfilling: This is an open dumping process of solid waste and a cost-effective method to dispose of waste. There are some negative impacts of landfilling, such as damaging biodiversity and water resources. So, it's crucial to consider these factors when choosing this method of disposal.
- Composting: It's a good method to convert waste into useful humus, and it helps with plant growth and conditioning the soil. It significantly reduces the amount of landfilling and has benefits in various ways. Different composting methods are there, such as onsite composting, vermicomposting, vessel composting, and windrow composting.
- Recycling: It's a process of transforming waste into useful products. Recycling is one main element in 3R, which is known as reuse, recycle, and reduce.
- Gasification: This method utilizes limited oxygen to convert a carbon-containing feedstock into a synthetic gas. Using these syngases as a starting point to manufacture fertilizers, hydrogen, methane, and liquid transportation fuels.
- Inertization: The process of mixing waste materials with cement and other materials in the proportion of 65% waste, 15% lime, 15% cement, and 5% water. This method is efficient in reducing the risk of toxic waste substances going into the surface and groundwater, which contaminates the water and land.
There are several other methods used in waste treatment and disposal, such as waste autoclave, wet and dry thermal treatment, microwave irradiation, incineration, and more. Organizations need to pay attention to utilizing these methods to effectively manage waste without harming the environment and individual health.
Latest Waste Management Technologies and Innovations
The ways waste is managed have been changing with the presence of the latest technologies and innovations. It's vital to utilize these latest technologies and trends to effectively manage waste in an organization.
These changes in technology and innovations not only help manage waste more efficiently but also ensure a greener sustainable future. Let's view some examples of these latest technologies and innovations:
- Smart Recycling Bins: These smart bins utilize sensors and data analytics to optimize waste collection, reducing unnecessary pickups and saving resources.
- Waste-to-Energy Processes: Some technologies help convert waste into useful energy, such as biogas production through organic waste residues, electricity, heat, or fuel production through methods such as pyrolysis, incineration, and gasification. These conversions are gaining traction as they help reduce landfill waste and generate power.
- AI-Driven Waste Sorting Systems: Artificial intelligence is making significant changes in the way we sort and recycle waste. With the help of AI, machines can swiftly identify and separate recyclables from non-recyclables. This makes the process more precise and less labor-intensive.
These innovations are some good examples of current trends in waste management, where staying informed about these trends leads individuals and organizations to play a part in shaping a more sustainable future.
Challenges in Effective Waste Management

Environmental Impact
Environmental impacts are a huge challenge for businesses when it comes to waste management. Waste management includes different stages, and at each stage, there are possibilities for environmental impacts. The challenges or impacts are identified as:
- Landfill emissions: When landfills are improperly managed, there are chances for greenhouse gas emissions or methane releases, which could significantly contribute to climate change.
- Soil and water contamination: Improper waste disposal can be the reason for contaminating soil and water, which may impact human health and the ecosystem.
- Air pollution: Waste releases bad odors and affects indoor air quality. Also, incineration presents smoke particles that can pollute the air in the atmosphere.
- Ecosystem Impacts: Improper waste disposal significantly impacts the ecosystem, wildlife, and biodiversity.
Resource Depletion
As the population continues to grow, resource utilization and waste generation are massive in numbers. Improper waste management practices lead to resource depletion, and addressing the challenge is vital.
Waste treatment methods like incineration and landfills are reducing the resources considerably, even when there are chances for recycling, reusing, or converting the waste materials into useful products such as biogas, compost, or any other.
Implementing proper strategies to mitigate resource depletion is crucial in establishing a sustainable future for the next generation.
Public Health Concerns
It's one of the most influential challenges in waste management, where public health is considered a very necessary parameter by the government and healthcare firms. Organizations face certain challenges when performing their tasks related to waste management, and they should be concerned about public health.
Improper waste management practices may lead to serious health issues that can cause legal issues for the business. Companies should follow all health-related considerations when managing waste, and it's necessary to avoid unnecessary challenges and consequences.
Legislative and Regulatory Hurdles
There are certain legislations and regulations that the government requires individuals and organizations to follow when managing waste. Such legislation and regulations protect the environment and human health from the adverse impacts of improper waste management.
It can be a huge hurdle for the organization to follow all regulations that are imperative from the government. However, it helps reduce adverse impacts. Therefore, this hurdle is somehow helpful to protect individuals, the environment, and organizations from certain impacts and legal issues. Understanding and complying with the regulations helps save organizations from legal issues. Here's why:
- Environmental Protection: Regulations related to environmental protection ensure that waste is managed in ways that minimize harm to the environment. They often set certain standards for waste disposal, storage, and transportation to prevent pollution and ecological damage. Example: The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the US governs the disposal of solid waste and hazardous waste.
- Workers and Public Health: Proper waste management practices protect the health of workers and the general public by reducing exposure to hazardous substances and preventing the spread of diseases. Example: Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards. OSHA is a federal agency that is responsible for ensuring safe and healthy working conditions for employees across various industries, including waste management.
- Reputational Risks: Non-compliance can lead to fines, legal problems, and reputational damage to a company. Complying with regulations is essential for long-term success. Example: The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) enforces the mandatory requirement to safeguard a company's reputation while practicing waste management.
Conducting Waste Audits for Improvement
When performing waste management tasks in an organization, it's unavoidable to be away from facing certain challenges. Companies successfully evade them by conducting waste audits, which help explore common mistakes, issues, and improvement opportunities. Here are some reasons why waste audits are necessary:
- Resource Efficiency: Waste audits help identify where important resources are being wasted, such as material waste, labor waste, and other resources. Identifying inefficiencies allows organizations to make significant improvements and reduce costs.
- Environmental Impact: Waste audits pinpoint the unnecessary waste in landfills and incinerators that can cause environmental impact. By identifying this, organizations can try to minimize waste and its environmental impact by utilizing the best alternative ways.
- Legal Compliance: The waste management practices should adhere to certain regulations, and different regions have different legal requirements. Waste audits highlight the important areas in which companies need to comply with the legal requirements.
Encouraging companies to conduct frequent waste audits helps mitigate waste management issues and enhance resource efficiency, reduce environmental impacts, and ensure legal compliance.
Career Opportunities in Waste Management

Waste Collection and Disposal
Proper waste collection and disposal are primary in every organization, which offers different employment opportunities as below:
- Garbage Truck Driver: This career is responsible for transporting the waste from the collection point to the disposal area. The garbage truck driver should be competent enough to drive the vehicle and be a responsible person to safely transport the waste from the generation point.
- Waste Collection Crew: This crew makes sure all waste in the workplace is collected appropriately and improves workplace cleanliness. The housekeeping team is an internal crew that collects waste and stores it in the storage. Workers from collection agencies or the government ensure the waste collection from the premises.
Waste Treatment and Recycling
Several waste treatment methods bring employment opportunities to individuals, such as:
- Recycling Specialist: This is a good career that helps recycle waste into a useful product, such as plastic production from waste materials. Recycling specialists should be competent enough and have adequate work-related skills to perform recycling operations on waste materials.
- Waste Treatment Plant Operator: This job is responsible for operating the waste treatment plant and ensuring that contamination is eliminated from the waste elements. Many waste treatment plants are there that produce useful products, such as biogas plants, composting plants, chemical disinfection plants, and other energy-producing plants. These plants include a plant operator career that requires the necessary skills to perform the tasks.
Environmental Compliance and Regulation
Waste management practices should comply with all kinds of environmental regulations, and below are some careers related to that:
- Environmental Consultant: This is a professional career where environmental consultants are responsible for ensuring that government regulations are complied with the waste management practices. Organizations should comply with the government rules and regulations related to environmental standards, where environmental consultants regulate these tasks.
- Waste Management Analyst: This particular career requires collecting and evaluating particular standards, data, and records related to waste management and making sure individuals and the environment are protected against adverse impacts. Waste management analysts mainly focus on analyzing important data and conducting audits to maintain a proper waste management system.
A Real-Life Case Study: Zero Manufacturing Waste to Landfill - A Model for Sustainable Waste Management in the USA
We can identify the importance of different waste management careers and practices that ensure sustainable waste management. Implementing the best possible waste management strategies helps reach this goal. Now let's see one such case study example in the USA:
Case Study: Procter & Gamble (P&G) - Zero Manufacturing Waste to Landfill
Background: Procter & Gamble (P&G) is one of the largest consumer goods companies in the USA, which set a sustainability goal to send zero manufacturing waste to landfills from its global network of plants. This smart objective demonstrated the company's commitment to environmental responsibility.
Challenges: P&G's manufacturing operations generated a huge amount of waste, including materials such as packaging, chemicals, and other byproducts. To meet the "zero waste to landfill" target, they required significant changes in waste management practices.
Approach: P&G implemented a multifaceted approach to achieve this goal:
- Waste Reduction: The company focused on minimizing waste at its source by improving product design, ensuring production quality, and achieving zero defects. They reduced packaging materials and optimized manufacturing techniques.
- Recycling and Reuse: P&G established some good recycling and reuse programs within its facilities. Materials that couldn't be eliminated were diverted from landfills and redirected toward recycling and recovery.
- Waste-to-Energy: Waste materials that couldn't be recycled or reused were converted into energy through a proper implementation of waste-to-energy technologies, which reduced the environmental impact.
Results: P&G's commitment to "zero waste to landfill" paid off significantly:
- By 2020, 86 percent of its global production sites achieved “zero manufacturing waste to landfill” status.
- The company could able to save millions of dollars in waste disposal costs.
- P&G's efforts helped in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing the environmental impact of its operations.
- This initiative not only aligned with P&G's sustainability goals but also enhanced its reputation as an environmentally responsible company.
Lessons Learned: Procter & Gamble's journey toward “zero manufacturing waste to landfill” is a great example that showcases the potential for businesses to make substantial contributions to environmental sustainability while performing waste management.
By integrating waste management strategies that emphasize waste reduction, recycling, and responsible disposal, companies can reduce their environmental footprint while reaping financial benefits. This case study from the USA serves as an inspiring example of how commitment to sustainability drives positive change while practicing waste management.
Skills and Qualifications for a Career in Waste Management

Educational Background
Waste management careers are performed at different levels, and according to the level of the career, the educational requirements vary. For waste collection careers like truck drivers and collection crews, they don’t need a degree-level education. However, they should have the necessary skills and certifications, like a driving license, waste handling skills, etc.
Professional-level careers like environmental consultants, waste management analysts, and recycling specialists need degree-level education to perform their tasks better, whereas a master's or Ph.D. level can be even better to understand complex tasks in waste management and to perform them to a standard level.
Key Skills and Abilities
Apart from educational qualifications, waste management careers require specific skills and abilities to perform tasks better. These skills are as follows:
- Technical skills: Professionals need high technical skills to do waste treatment and other related duties. They need to understand the technical stuff in the processing of recycling, composting, chemical disinfection, and so on.
- Analytical and problem-solving: Professionals should have these analytical and problem-solving skills. This helps analyze the data accurately to make informed decisions related to waste management. Plus, solve problems with a strong ability for conflict management.
- Communication skills: Good communication skills are vital to performing waste management-related tasks. Professionals have to interact with many people and government staff when they perform these tasks. Therefore, this skill is mandatory for every worker.
- Leadership and management: Leadership and management skills are important to guide teams and set waste management goals and strategies. These skills can help manage the workforce better and drive organizational success.
Several other skills are necessary for waste management professionals to perform their work-related tasks, such as adaptability, environmental awareness, flexibility, and many others.
For further understanding, read this article related to the essential work-related skills and strengths of employees: https://smarttoolsai.com/post/10-essential-work-related-strengths-for-professionals
Advancing Your Career in Waste Management

Professional Training and Development
Career development is necessary for employees working in the waste management field. It's necessary to obtain professional training and development programs to make this career development possible.
Organizations should offer necessary professional training to the workers to make them competent. This enables them to perform better in their respective job areas. Further, these training and development programs positively impact employee performance and eventually result in quick task delivery and productivity enhancement.
Advancement into Management Positions
Organizations should motivate employees by offering advancement into managerial positions when they acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to perform duties in the best possible way. This is vital to acquire the best talents in the organization internally and to establish a proper working culture.
Moreover, Employees feel valued when they get promoted to managerial positions, where they strive hard to perform their duties according to the standards.
Benefits of Working in Waste Management
Contribution to Environmental Sustainability and CSR
It's the most obvious benefit brought by professionals working in waste management. A proper waste management practice ensures environmental sustainability by contributing to sustainable practices and standards.
Ensuring proper waste management leads the company to corporate social responsibility (CSR) that benefits the organization to enhances its reputation among the general public. In simple words, when a company thinks about the environment and social factors while doing waste management, it gets huge respect and popularity among the public.
Moreover, mitigating resource depletion and safeguarding biodiversity are more important concerns for waste management workers. They contribute to a better future for the next generation by safeguarding resources that are reused, recycled, or converted into useful products without going into landfills.
Job Stability and Demand
Careers in waste management have constant demand and job stability. This is because these careers are service-level jobs that require hard work and dedication. People who work in waste management tend to have high demand, and they work with diligence to upgrade the value of an organization and its surroundings.
For these reasons, organizations value these professions and stabilize job security for the long term. Also, employees take fewer days off and make fewer mistakes in this particular job area, where making mistakes and frequent day-offs can significantly impact the entire business and human health. Therefore, the risk of getting fired is minimal.
Opportunities for Innovation and Growth
There are ample opportunities provided for workers for innovative thinking and growth in the field of waste management. People come up with the best innovations in reducing waste in the organization, and implementing the best treatment or disposal strategies is valued by the management.
These innovations and strategies make a significant impact in establishing the finest waste management practice in the organization. It brings a cohesive working environment to the staff and introduces the best opportunities for further growth in their respective professional area.
Final Thoughts
Waste management is a crucial function that every organization should pay attention to effectively manage their waste without impacting human health and the environment. It brings ample benefits to the organization and society by enhancing the organization’s productivity and social responsibility.
The waste management process involves different stages such as waste collection, storage, transportation, treatment, and disposal, which involve different tasks in each stage. There are various waste treatment options available to properly handle waste and convert it into a useful product.
Certain careers have high demand in this sector, where people are well paid and given priority for the intricate waste management jobs. There are career advancement opportunities that are based on the competence level of the employees, which boosts their performance.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main stages involved in waste management?
The main stages of waste management involve waste collection, storage, transportation, and treatment or disposal.
Q2: What are the different types of waste that need efficient handling?
Various types of waste, including solid waste (papers, plastics, metals), hazardous waste (chemicals, electronic residues), and organic waste (food scraps, peels), need efficient handling.
Q3: What is the regulation of waste management in the US?
Waste management in the US is regulated by various laws and agencies, such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), which sets standards for waste disposal, storage, and transportation to protect the environment and human health.
Explore Related Articles
https://smarttoolsai.com/post/length-converter-in-apparel-construction-and-other-key-industries
.webp)