
Common Risks in Healthcare: An In-Depth Guide to Effective Risk Mitigation
What makes a hospital different from a typical office building? Beyond the obvious presence of patients and medical equipment, healthcare firms stand apart from other sectors due to their unique and complex risk nature. This is why every organization within healthcare must navigate various types of risks that can be broadly classified as:
- Fire
- Electrical Hazards
- Working at Height
- Excessive Noise Level
- Hazardous Substances
- Insufficient Welfare Facilities
- Manual Handling
- Substance Abuse
- Work-Related Stress and many more
Healthcare firms must effectively address these risks to protect their occupants from harmful exposures and incidents. Also, managing these risks is crucial for improving productivity. By prioritizing risk mitigation, healthcare firms can safeguard both their people and operations against unexpected, adverse events.
Article Overview
- Understand the unique and complex nature of risk management in healthcare.
- Learn the importance of mitigating risks to ensure the safety of healthcare staff, patients, and visitors. Plus, identify the consequences of not addressing them.
- Explore common healthcare risks such as flammable medical gases, excessive noise, hazardous waste, electrical risks, etc.
- Discover strategies for mitigating risks with detailed control measures and recognize the benefits of effective risk mitigation.

The Importance of Healthcare Risk Mitigation
Healthcare firms face significant workplace risks where occupants need adequate protection. Implementing proper risk mitigation measures is vital to maintain safety for the healthcare staff, patients, visitors, and others. Failing to do this may cause severe problems such as reputational loss, accident downtime, legal compensation, and financial losses.
Generally, people like to visit safe places that are free from risks. This is another crucial reason to mitigate risk events. Further, every firm should understand the importance of mitigating risks and providing a safe place to work, visit, and get treatment.
Detailed Analysis of Common Healthcare Risks
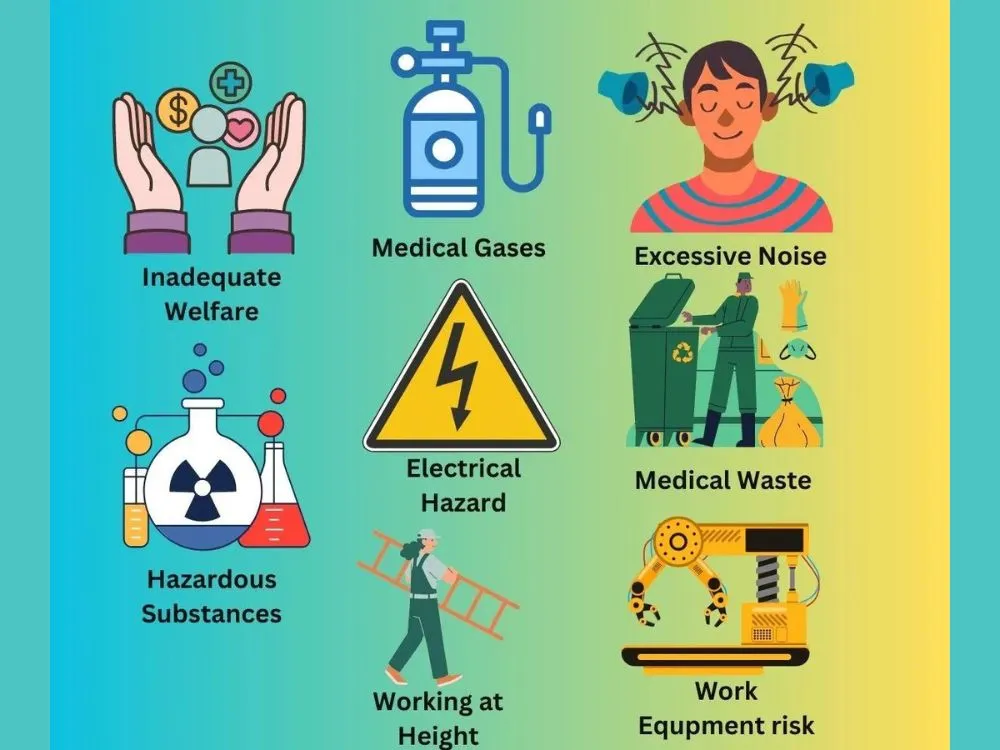
Risk 01- Flammable Medical Gases and Fire
In healthcare sectors, medical gases are used for various purposes such as providing ventilation, performing operations, etc. Many types of medical gases are used in healthcare facilities like oxygen, nitrogen, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, and vacuum.
These medical gases are highly flammable and need special attention to avoid fire incidents. Plus, it's vital to maintain them with proper care because the risk they pose is catastrophic. Improper maintenance can impact the entire facility, which can lead to fire and explosion.
This may lead to severe consequences for the occupants. For example, fire burns, injuries, asphyxiation, and in the worst case scenario, death.
Risk 02- Excessive Noise Levels and Their Impact
The noise level should be bearable by anyone inside the healthcare facility. It can be a serious risk for all occupants if it exceeds the standard bearable condition. The main contributor to excessive noise levels is generators. They emit more than 85 decibels (dB) of sound that cannot be tolerated by any human being.
Also, it impacts the people who mainly handle generator maintenance. They visit the generator room more often to check its functionality. Additionally, the people in the areas nearby can be impacted by this sound emission.
This may cause many health-related problems. Some such problems are known as temporary hearing loss, Tinnitus, discomfort, headaches, and worst-case scenarios that can cause noise-induced deafness (NID) in prolonged exposure.
Risk 03- Hazardous Medical Waste Generation
Healthcare industries generate high levels of hazardous medical waste, such as expired pharmaceuticals, sharps, infectious biological waste, and pathogens. This medical waste is a serious risk that can cause severe problems to the waste handlers and people who are likely to be exposed.
Until the hazardous wastes are collected by the authorized waste collection agents or companies, they are stored and handled by the internal janitorial staff, where they have a higher risk of exposure.
The exposure is possible through skin absorption, inhalation, and biological and accidental ingestion of expired drugs. It can cause severe acute and chronic health impacts like pain elevation, acute toxicity, nausea, liver damage, allergies, and immunity damage.
Risk 04- Electrical Risks
In healthcare facilities, some most common electrical faults include portable electrical equipment defects, wet floors, misuse of electrical equipment, and unavailability of lockout and tag out (LOTO) procedures. These common faults may lead to electrical risks like exposure to electric shocks or electrocution.
Touching faulty portable electrical equipment, misusing equipment like inserting wires into the sockets directly without a plug, and working on wet surfaces are some practices that expose people to electrical risks.
The most common consequences of electrical risk exposure include painful sensations, muscle contractions, electric shocks, falls, electrical burns (direct or indirect), fainting, and in severe cases, death.
Risk 05- Working at Height
On several occasions, staff and other external people, such as contractors, work at height in a healthcare building. Whether it's a maintenance job or a cleaning job, working at height cannot be avoided. Also, negligence or unawareness can lead to serious risk occurrences.
Cleaning staff are required to clean higher surfaces that can only be accessed by using a step ladder. Also, maintenance staff perform maintenance duties on higher surfaces where necessary precaution is needed to avoid falling.
There can be open areas without protected edges or uneven surfaces that are dangerous. They tend to cause a risk of falling. The consequences of falling are injuries, fractures, bruises, paralysis, and fatalities.
Risk 06- Inadequate Welfare Facilities
Providing necessary welfare is the primary responsibility of the employer. Insufficient welfare provision can lead to multiple problems. Welfare facilities such as washrooms, dining areas, adequate workspace, drinking water, restrooms, uniform changing facilities, washing, and other facilities are mandatory to be provided at the premises.
Failing to provide these facilities will result in risks related to health and well-being. Consequences of inadequate welfare provision are work-related stress, productivity losses, mental health effects, fatigue, anxiety, and other ergonomic issues.
Risk 07- Managing Hazardous Substances
The presence of hazardous substances in healthcare facilities, such as housekeeping chemicals, mercury, toxic drugs, pesticides, and laboratory materials, poses significant risks. These substances must be handled, stored, and used with utmost care to ensure safety.
Proper labeling is also vital for easy identification. Failing to follow these rules may lead to the risk of exposure to dangerous chemicals. Hazardous substances can cause acute and chronic health issues through inhalation, skin absorption, or accidental consumption. Further, the consequences are skin irritation, burns, nausea, dermatitis, and organ damage.
Risk 08- Risks Associated with Healthcare Equipment
Mechanical and non-mechanical machinery hazards are important to consider. These machinery-related risks are serious and cause severe damage. In healthcare facilities, several work-related equipment are available, and improper guarding and maintenance can lead to potential risk.
For example, when it comes to boiler maintenance, staff should perform proper maintenance activities to prevent risk occurrences. If they fail to do maintenance properly, it may lead to non-mechanical hazards such as carbon monoxide emission, fire, and explosion.
This carbon monoxide emission can cause asphyxiation, dizziness, and organ damage. Fire or explosion risk is possible to occur when the boiler equipment is operated in an imbalanced pressure or low water conditions.
Strategies for Effective Risk Mitigation in Healthcare
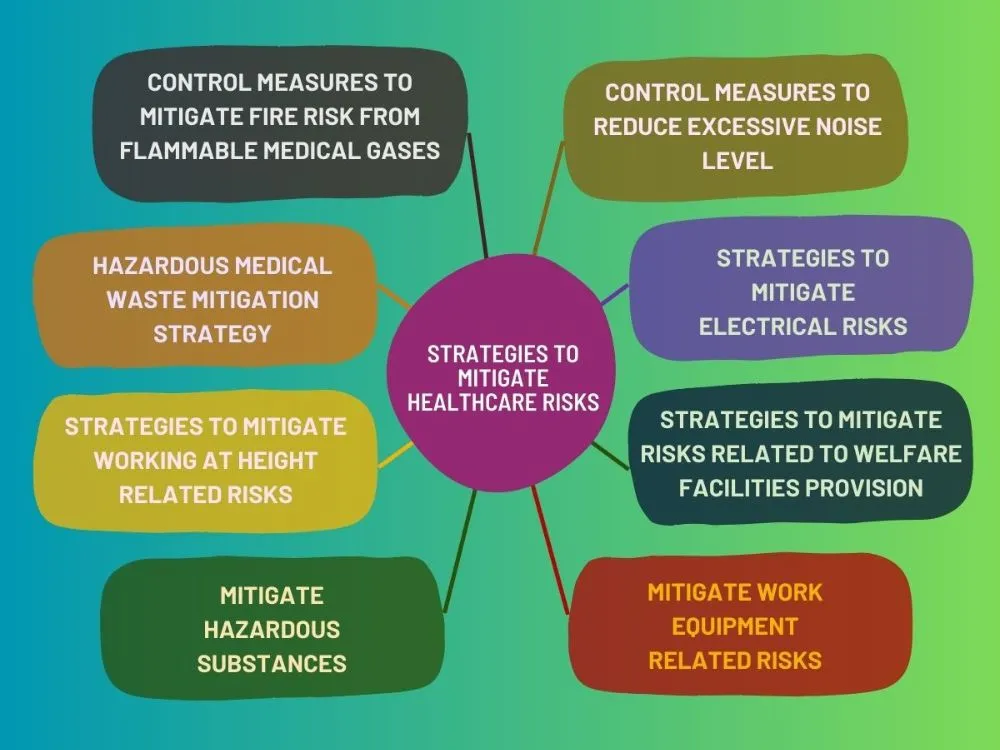
A) Control Measures for Flammable Medical Gases
To mitigate fire risk from flammable medical gases, a healthcare facility must implement the necessary control measures as below:
- Conduct training for the engineering and maintenance staff to handle, transport, and store the gas cylinders carefully.
- Print and affix appropriate warning signs (Highly flammable gases, do not smoke, no hot work) in respective gas storage areas to avoid any kind of ignition activities near the gas cylinders.
- Implement a checklist for operational checks of safety valves and other components to prevent pressurized vessel blasting.
- Separately store the empty cylinders from the full-cylinder gas bank store.
- Proper maintenance of gas cylinders and regular check of pressure level (for example, 04 bar pressure is maintained for O2 cylinders).
- Arrange fire protection systems like sprinklers, fire hydrants, hose reels, and different types of portable fire extinguishers like CO2, water, foam, and ABC dry powder in every area. This helps suppress fire in case of a fire occurrence.
- Train and educate the staff in emergency fire circumstances, safe evacuation, fire type, appropriate extinguisher usage, and dos and don’ts (ex, Avoid using elevators when there is a fire in the building).
B) Reducing Excessive Noise Levels
The following control measures are applicable to mitigate the risk of excessive noise levels in a healthcare facility:
- Install Noise suppressors or silencers to reduce the noise level.
- Procure a noise meter to measure the sound level. Plus, a complete noise level assessment should be done by a competent person.
- An audiometry test should be done on the staff by a competent person to find out if any previous or new hearing damage has occurred. This helps rectify the issue.
- Necessary training and information should be provided regarding generator maintenance and safety concerns.
- Proper and timely maintenance of the generator equipment. The daily checklist includes checking of diesel level, oil level, meters, gauges, batteries, cleanliness, equipment grounding, and vibration.
- Walls, doors, and other components of the generator machine room should be with sound-insulating materials or soundproofed.
- Provide and mandate the usage of hearing protection when entering the generator room, and make sure maintenance staff wear it regularly.
- Introduce daily shifts or work rotations to the electrical maintenance staff to avoid recurring exposure and monitor their activities.
C) Mitigating Hazardous Medical Waste
Strategies that healthcare facilities can follow to mitigate the amount of hazardous medical waste generation are as follows;
- Installation of an incinerator to destroy medical waste.
- Implement work rotation and shifts for housekeeping staff to reduce medical waste exposure time.
- Arrange proper waste segregation methods to segregate medical wastes from other general hospital wastes (Separate medical waste storage area and color-coded bins with proper labels).
- Regular monitoring of the staff, whether they maintain personal hygiene before, during, and after handling medical waste.
- Introduce proper waste management processes from waste generation to effective disposal.
- Introduce periodical health surveillance for the waste handlers to find health issues and implement rectification. If necessary, provide paid time off for workers to reduce exposure.
- Implement proper computerized stock management for pharmaceuticals and timely disposal of expired pharmaceutical items.
- Use necessary PPEs such as gloves, aprons, masks, and safety shoes when handling medical waste.
D) Managing Electrical Risks
Mitigating electrical risks is crucial in healthcare facilities to avoid unnecessary consequences in the building. The following strategies are effective in controlling electrical risk:
- Implement proper lockout and tag-out procedures on the isolator to secure the system before doing maintenance on the dead system.
- Timely maintenance of electrical components such as panel boards, main switch boxes, transformers, ATS panels, etc.
- Installation of protective devices such as electrical circuit breakers, RCD, fuses, grounding, stabilizers to control voltage fluctuations, etc.
- Repair the defects in portable electrical equipment and protect the conductors adequately with double insulation.
- Always follow a safe system of work (SSOW) methods like avoiding inserting wires into the socket without a plug, avoiding using electrical equipment with wet hands, etc.
- Do regular mopping or wet/dry vacuuming to dry the wet floor.
- Clean and remove dust inside the electrical panel boards every month using a blower to prevent malfunctioning.
- Affix warning signs in critical areas with potential electrical hazard descriptions.
- Authorized access to the electrical panel room, UPS, and generator room.
- Provide necessary PPEs like boots, helmets, safety gloves, etc.
E) Ensuring Safety While Working at Height
To control risks related to working at height, the following strategies are implemented:
- Check and maintain the ladders often.
- Procure a pole cleaning kit to clean the windows, top surfaces, and components by standing on the floor instead of using a step ladder.
- Permanently protect the open edges using guardrails.
- Proper housekeeping to prevent slippery floors and obstructions.
- Using relevant signboards when performing maintenance and cleaning works at height.
- Provide necessary training and instructions to the workers with practical illustrations regarding unsafe behaviors of working at height.
- Provide safe working practices for using ladders safely. Always check the stability of the ladders before usage and follow proper safety precautions.
- Random supervision is necessary to find out unsafe behaviors of staff when working at height.
- Provide necessary PPEs such as safety helmets, shoes, gloves, and masks to work at height.
F) Improving Welfare Facilities
Strategies below in a healthcare organization can improve the provision of welfare facilities. This helps mitigate risks related to inadequate welfare provision:
- Arrange a breakout room facility for the staff to rest. Facilitate with hazard-free and properly ventilated workplace.
- Proper space arrangement and decluttering. Also, arrange stationery properly.
- Improve sanitary facilities to match the number of occupants.
- Do proper housekeeping and follow a washroom checklist to clean and prevent unnecessary odors and unpleasant smells.
- Ensure to provide proper washing, dining, and other necessary facilities as per the requirements. This helps reduce crowding and queuing to use facilities.
G) Handling Hazardous Substances
It's important to mitigate the risk of hazardous substances where chemicals are more dangerous. The following strategies are used to effectively control the risk presented:
- Authorized access to the housekeeping store.
- Conduct toolbox talks and training to instruct housekeeping staff on safe working practices.
- Use proper storage containers to store chemicals and label them correctly.
- Always follow proper hygienic practices when using housekeeping chemicals for cleaning.
- Always tightly close the containers to prevent spillages or accidental release of chemical contents.
- Proper Storage and warehouse management to avoid dumping.
- Monitor the janitors' work whether they follow safe work practices when doing cleaning.
- Use relevant PPEs to avoid contact with chemical content.
H) Mitigating Work Equipment-Related Risks
The mechanical and non-mechanical risk presence of critical work equipment can be effectively controlled by following these strategies:
- Regular inspection of critical work equipment.
- Periodic and annual maintenance should be conducted without delays.
- Proper machine guarding is necessary to avoid accidents.
- Initiate a planned preventive maintenance program to maintain the equipment in top condition.
- An electronic access control system (Proximity electronic cards or biometric door locks) should be installed to avoid unauthorized access to the machine or plant room.
- Issue and mandate of wearing necessary personal protective equipment like gloves, respirators, and hearing & eye protection. This helps avoid any exposure when working with machinery.
Final Thoughts
Ensuring workplace safety in a healthcare facility is crucial for protecting both occupants and the organization's assets. This article highlights common risks in healthcare buildings and outlines effective strategies for mitigating them.
Implementing proper risk mitigation measures provides healthcare organizations with numerous benefits. It includes safeguarding their reputation, preventing accidents, avoiding legal liabilities, reducing costs associated with incidents, and minimizing investigation time.
FAQs
Q1: What are the common risks in the healthcare industry?
Common risks in healthcare include fire hazards, electrical risks, excessive noise levels, hazardous substances, working at height, inadequate welfare facilities, generation of hazardous medical waste, and more.
Q2: Why is healthcare risk mitigation so important?
Healthcare risk mitigation is crucial to protect the safety and well-being of healthcare staff, patients, visitors, and other individuals. Failing to mitigate risks can lead to reputational loss, accidents, legal complications, and financial losses.
Q3: What is risk prevention in healthcare?
Risk prevention is also known as risk avoidance. It involves effectively eliminating the sources of potential risks. In healthcare facilities, this is achieved through the implementation of proper elimination techniques to address these risks at their source.
Explore Related Posts
https://smarttoolsai.com/post/risk-management-plan-for-your-high-risk-business
.webp)