
Physical Asset Management for Wealth Maximization: A Strategic Guide to Financial Success
Think about how companies keep their buildings, equipment, and vehicles running smoothly every day. That's the magic of physical asset management, a crucial part of making sure everything operates without a hitch.
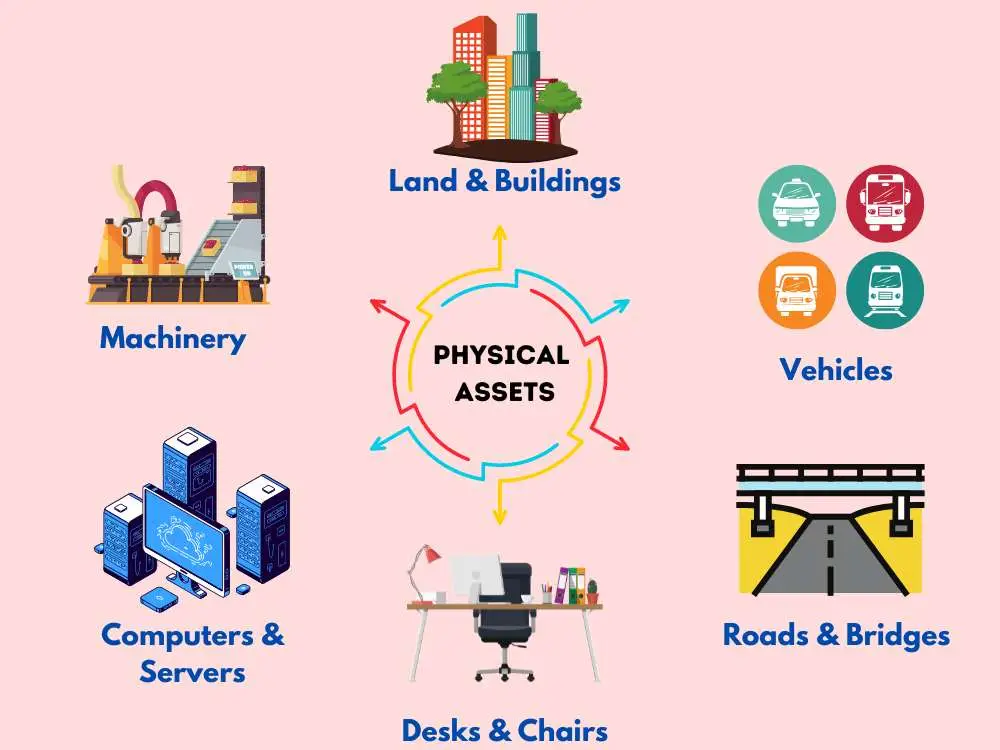
Every organization has different types of physical assets that are used for operational procedures. These assets are tangible and commonly identified as:
- Fixed Assets like Land and Buildings
- Moving (Mobile) Assets like Vehicles
- Machinery Assets
- Digital Infrastructure (Assets Related to IT) like Computers, Servers, and Network Equipment
- Furniture and Fixtures like Office Desks and Chairs
- Infrastructure Assets like Roads and Bridges
Organizations need these assets for manufacturing and operational procedures. Plus, businesses need to manage them effectively. Therefore, physical asset management (PAM) involves certain procedures for managing the assets of an organization. It helps effectively manage assets' lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
Moreover, PAM helps maximize the asset value and reduce risks and costs during the whole life cycle of assets. For example, from their creation phase to their maintenance, operation, and eventual disposal or replacement phases.
The goal of PAM is to enhance the availability and reliability of an organization's physical assets while reducing maintenance costs and optimizing resource usage.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of physical asset management for ensuring smooth daily operations and asset lifecycle management.
- Learn about the different types of physical assets, including fixed, mobile, machinery, IT, furniture, and infrastructure assets.
- Explore strategies for effective physical asset management, such as asset identification, evaluation, maintenance, and risk mitigation.
- Discover how physical asset management can maximize wealth through asset appreciation, capital preservation, income generation, and tax planning.
- Recognize the challenges in physical asset management, including market volatility, economic uncertainty, and regulatory compliance.
An organization should properly manage its physical assets because it directly supports wealth maximization. The physical assets have a depreciation value, and getting optimum benefits from the assets is only possible through a good asset management system.
Effective PAM helps minimize unnecessary costs that are spent on assets. For example, costs like reparation, depreciation, and replacement. It also enhances assets’ performance, which leads to good productivity and wealth.
PAM is useful to find out underutilized assets in an organization that can be sold to generate an income. Also, it helps improve operational efficiency, profitability, and financial success. By making sure all physical assets are managed properly, an organization can maximize its wealth potential and reach its financial goals.
Understanding Physical Asset Management
Characteristics of Physical Assets
Unlike intangible assets such as company reputation, brand, pattern, and trademark, the characteristics of physical assets are diverse, as these assets are tangible and have a market value.
As we know, physical assets are movable assets or fixed assets that have a finite lifespan. They depreciate and lose value over time. Therefore, they require proper regular maintenance to be kept in an optimum condition.
The market value of physical assets is subject to change according to many factors. Understanding all of these vital characteristics of physical assets is important to develop efficient asset management strategies for optimum asset utilization.
Types of Physical Assets
Organizations rely on various physical assets, each playing a crucial role in their operations:
- Fixed Assets: Land and structures provide the foundation and space for business activities.
- Movable Assets: Vehicles and inventories facilitate transportation and stock management.
- Machinery: Essential for production and operational processes.
- Digital Infrastructure Assets: Vital for modern business operations and communication.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Necessary for a functional and ergonomic workspace.
- Infrastructure Assets: Support broader organizational activities and logistics.
While lands are permanent, other assets have a lifespan and depreciation value. Proper maintenance is essential to preserve their value and functionality, which directly contributes to the business's success.
The Goal of Physical Asset Management
The main goal of PAM is to enhance the availability, reliability, and profitability of an organization's physical assets. By reducing maintenance costs and optimizing resource usage, organizations can ensure their assets continue to support their business needs effectively.
In simple terms, every organization's primary goal is to maximize its wealth through effective asset utilization in its lifecycle.
Benefits of Physical Asset Management
PAM encompasses the necessary stages of assets that exist in the organization during the asset lifecycle. Implementing a consolidated physical asset management system can benefit the organization in multiple ways. It leads an organization to optimize the usage of its assets with minimal risk and costs.
Also, it helps increase asset lifespan by performing necessary maintenance. Having a good asset management system can enhance operational efficiency and help comply with all industry standards and regulations. Further, organizations can plan investments and get maximum returns for what they invest in physical assets.
Effective Strategies for Physical Asset Management
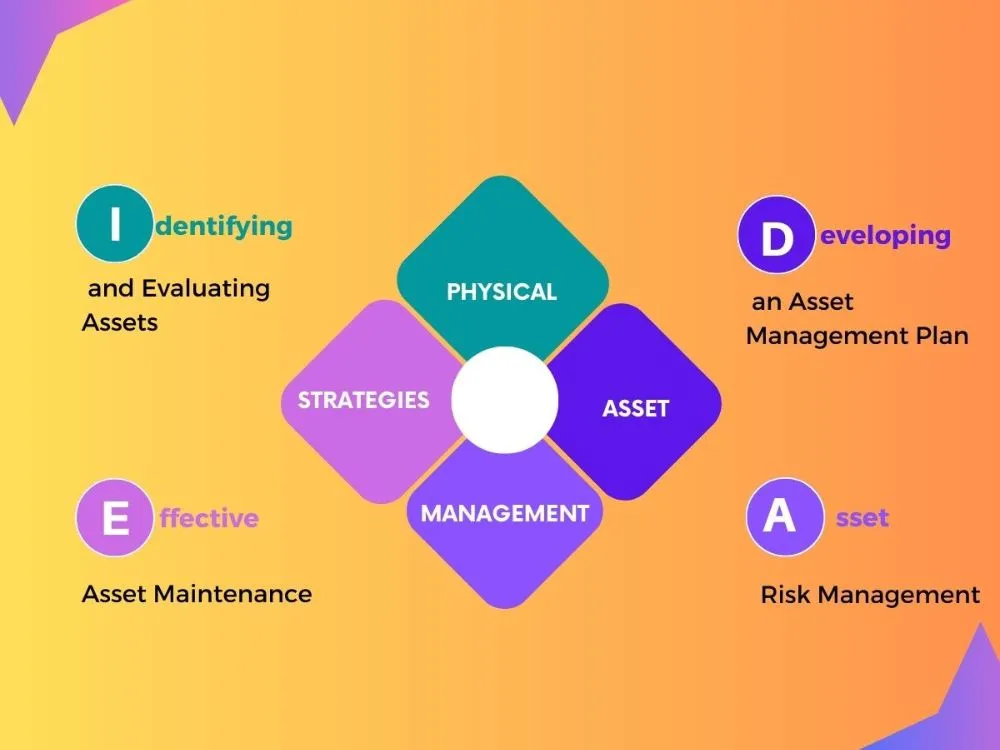
Identifying and Evaluating Assets
Organizations follow and implement various strategies to perform efficient physical asset management. One such strategy is identifying and evaluating the assets of an organization. This approach provides clear insights about asset condition, value, and potential risks.
This information is crucial in making vital decisions like whether to keep the assets or repair them, replace them, or dispose. It also allows efficient resource allocation and reduces downtime. Various methods are followed to perform asset identification and evaluation, like asset tagging, data collection, and regular inventory audits.
Developing a Comprehensive Asset Management Plan
By developing a comprehensive asset management plan, business organizations can able to plan and address their assets with proper care. It's important to understand the asset’s condition and lifecycle before developing a successful asset management plan.
An asset management plan helps organizations keep their assets in optimum condition. For example, a thorough asset management plan is necessary to be conducted on time. For example, asset maintenance, repair, replacement of spare parts, etc.
When developing an asset management plan, it's vital to collaborate with teams in an organization. Plus, a well-developed asset management plan improves asset lifespan and reduces unnecessary costs.
Enhancing Asset Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Effective asset maintenance enhances asset performance and lifespan. This will reduce issues related to asset malfunctioning or downtime. Professionals perform different types of maintenance, such as preventive, predictive, or corrective maintenance, to keep the asset in an active usable condition.
Corrective maintenance involves solving issues when there is a problem arises. It's better to perform preventive and predictive maintenance to effectively prevent asset failures. Corrective maintenance only works well when there is an asset malfunction that needs immediate correction or solution.
This maintenance for physical assets is required to be done at frequent intervals. Plus, the money spent by an organization on maintaining the assets can save huge costs of asset failures and downtime.
Mitigating Asset Risks Through Proactive Management
One of the essential strategies for PAM is asset risk management. It involves identifying potential risks and threats to physical assets and arranging proper measures to mitigate them.
Some most common risks an organization encounters related to its assets like asset failure, theft or vandalism, natural disasters, difficulties in finding asset repair parts, etc. Organizations can apply necessary risk management strategies that can control asset-related risks and ensure continuous functionality.
Maximizing Wealth through Physical Asset Management
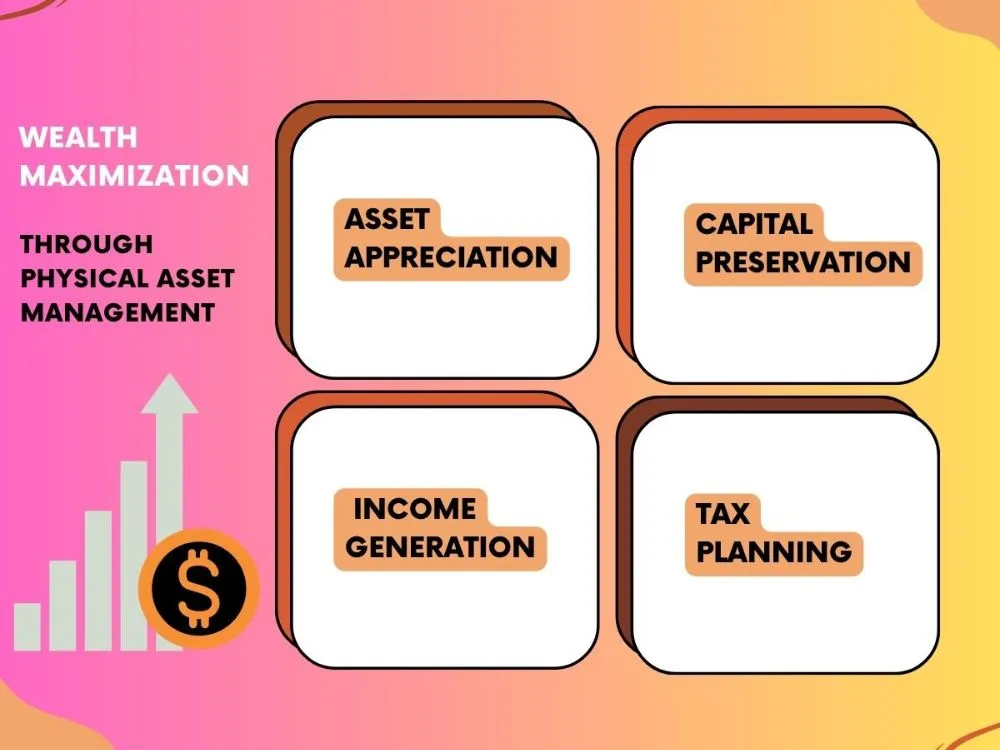
Asset Appreciation: A Path to Wealth Maximization
Asset appreciation is the process of increasing the physical asset value over time. It can be a crucial factor in maximizing the wealth of an organization. Asset appreciation is performed in various ways, such as making a vital improvement on the asset, enhancing market demand, and proper place (location) selection.
For example, an asset like a hotel building is more valuable in urban areas than in rural areas. Plus, improvements such as installing additional features or facilities in the hotel can enhance its value.
By appreciating the asset value, the organization gains many wealth benefits such as increased profitability, net worth, and market share. Hence, it's important to note that asset appreciation needs careful attention when planning and managing the assets.
Capital Preservation Strategies
Preserving capital will always remain a primary objective, and this entails protecting the assets of an organization and avoiding unnecessary risks that may result in losses. One practical approach to fulfill this goal is to invest in tangible physical assets.
These assets always appreciate over time and offer a long-term value that can withstand market fluctuations. Also, physical assets may serve as a barricade against inflation since their value generally increases with the rising cost of living.
By adopting a capital preservation-focused strategy for managing physical assets, organizations can effectively create and safeguard wealth for the future.
Income Generation Through Asset Utilization
Generating income and maximizing the profit of an organization is possible through different asset utilization methods. If an organization has multiple assets, it can generate income by renting out spaces or vehicles and selling assets for a profit.
Physical assets appreciate over time, and they are easily sold with adequate profit. Also, using physical assets, an organization can manufacture good-quality products that can generate substantial income. Moreover, planning the assets to maximize utilization and, in return, grow the wealth of an organization is invaluable in the PAM procedure.
Tax Planning for Long-Term Wealth Growth
To gain maximum wealth through PAM, it's vital to implement a complete tax planning strategy. Effective tax planning influences the long-term growth and resilience of an organization's wealth. This entails competent calculation of tax values when making investment options and choosing assets for inclusion in a portfolio.
Also, it involves structuring an organization's assets in a manner that reduces tax liabilities and capitalizes on available tax benefits, such as deductions and credits. Organizations optimize their PAM and enhance their overall wealth by collaborating with tax experts and utilizing strategic tax planning approaches.
Challenges in Physical Asset Management

Navigating Market Volatility
One of the biggest challenges faced by organizations in PAM is market volatility. According to a fluctuating global economy, it significantly impacts the value of physical assets. Moreover, it's a great challenge for managers to forecast market trends and implement asset management strategies relevant to them.
Further, market volatility influences drops and rises in assets' demand and supply, which can affect the value of assets. Failing to find out the volatile condition of the asset market may lead to a great loss. Organizations should focus on identifying the volatile market conditions to successfully face this challenge.
Managing Economic Uncertainty
Economic uncertainty for physical assets is a big challenge to managing them. Economic conditions are hard to predict and fluctuate from time to time. Various economic factors can influence the condition of physical assets, such as demand, supply, asset price, depreciation, technology, alternative goods, and many more.
These economic factors are uncertain and challenging to properly plan, budget, and invest in physical assets. It also leads to high maintenance costs and inefficient resource allocation. Therefore, it's essential for an organization to carefully handle its asset management relevant to the challenging economic conditions.
Compliance with Shifting Regulations
Compliance management is crucial because government regulations are vital to follow. Failing to adhere to government rules and regulations leads to many problems, such as fines, shutdowns, and imprisonment. An organization may have several assets, and every asset has its own regulations to avoid accidents and asset-related issues.
For example, vehicles owned by an organization should pass the emission test, buildings that are mandated with certain regulations, and production equipment with appropriate regulatory compliance.
The asset management strategy should comply with government regulations, and it frequently changes. Therefore, organizations need to be vigilant to face this challenge to avoid unnecessary issues and uphold their asset value and ensure success.
Wrapping Up
Effective physical asset management (PAM) is important for wealth maximization. By understanding the characteristics of assets and implementing strategies for identification, evaluation, and maintenance, organizations can optimize value and minimize costs.
Maximizing wealth can be achieved through asset appreciation, capital preservation, income generation, and tax planning. However, challenges such as market volatility, economic uncertainty, and regulations must be addressed.
Adopting technology and proactive maintenance practices can shape the future of asset management. Plus, by staying informed and adapting to industry trends, organizations unlock the full potential of their assets and maximize wealth.
FAQs
Q1: What is physical asset management?
Physical asset management refers to the method of effectively managing tangible assets throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal, to maximize their value and minimize costs and risks.
Q2: Why is physical asset management important for wealth maximization?
PAM is essential for wealth maximization as it helps organizations optimize asset utilization, reduce unnecessary costs, improve operational efficiency, and reach their financial goals.
Q3: What are the key benefits of physical asset management?
Implementing a comprehensive physical asset management system offers several benefits, such as optimized asset usage, increased lifespan through maintenance, improved operational efficiency, compliance with regulations, and maximum returns on asset investments.
Q4: How can physical asset management contribute to income generation?
PAM can contribute to income generation by renting out spaces and vehicles, selling assets for profit, and utilizing assets for manufacturing products that generate revenue.
Q5: What are the challenges in physical asset management?
Some challenges in physical asset management include market volatility, economic uncertainty, keeping up with changing regulations, and low liquidity. Organizations need to navigate these challenges to ensure successful asset management and wealth maximization.
Q6: What are examples of physical assets?
There are various types of physical assets, and they can be tangible. The most common physical assets are identified as land, buildings, vehicles, machinery, and other inventories.
.webp)