.webp)
Money Talks: Gross Profit Decoded for Entrepreneurs
The primary goal of every entrepreneur is to maximize the profitability of the company as well as to sustain the business for a long period. Profit is the lifeline of a company, and it plays an important role in a business's survival.
A non-profitable business may create numerous problems for entrepreneurs. Profits are broadly classified into gross profit and net profit. For entrepreneurs, knowing gross profit isn't merely important but necessary.
This measure becomes more of a vital sign for businesses. It drives the key strategic decisions of an organization toward growth and sustainability. Understanding gross profit will help the entrepreneur decipher a metric to set optimal prices, detect and reduce inefficiencies in products or services, and maximize business growth.
Key Takeaways
• Understand what gross profit is, the method to calculate it, and why it is essential for measuring business profitability and sustainability.
• See how gross profit helps in making key business decisions related to cost control, pricing, and financial planning.
• Learn key elements of gross profit like revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS). Plus, understand how to figure out gross profit and gross profit margin.
• Discover how using gross profit data can guide business choices, highlight areas needing improvement, and aid in communicating with investors and stakeholders.
• Recognize common errors in gross profit calculation and interpretation. Plus, understand the need to look at other financial indicators for a complete view of business health.
How Gross Profit Serves as a Critical Financial Indicator for Businesses
Gross profit functions as a critical financial indicator for businesses in different ways. It's a prominent index that showcases how well a business is generating profit from sales and revenue. Here are some important strategic decisions that businesses make utilizing gross profit as an indicator:

- Profitability Assessment: Gross profit is a direct indicator that reveals a business’s profitability. By assessing profitability, businesses can effectively plan their upcoming sales and revenue growth.
- Cost control and efficiency: Gross profit indicates the level of cost that has been spent on production and goods sales. It helps optimize costs and regulate unnecessary spending. It also improves efficiency by mitigating cost inefficiencies.
- Pricing strategies: It's important to set an optimum price for the products or services that help increase sales. Here, gross profit is a vital indicator to make necessary pricing strategies in an organization.
- Financial decision-making: Gross profit is a crucial financial indicator that lets entrepreneurs make financial decisions effectively, such as budgeting, investment planning, and financial forecasting.
- Investor and stakeholder insights: Gross profit provides an indication to the investors and stakeholders about the financial status and stability of the business. This helps make financial planning and growth.
Understand Gross Profit

What is Gross Profit?
Gross profit is known as a business’s profit before tax payments and other operating costs of a business. There is a clear difference between the revenue generated from the sales of goods or services and the cost of particular inventory items that the business sells.
It's a great financial indicator that businesses require to make informed financial decisions and plan their sales and revenue decisions. Gross profit is an invaluable indicator that effectively indicates a business’s ability to generate revenue throughout all its primary operations. It's often used for financial analysis.
Gross Profit vs Net Profit
Both are valuable financial metrics for a business to make informed financial decisions. They differ from the calculation, where gross profit only considers business sales and costs of goods sold (COGS).
Net profit is calculated by deducting all operating costs and other expenses, such as tax and insurance, from the gross profit. Net profit indicates the final profit value of an organization after all expenses have been deducted. It's added to the equity of the balance sheet.
In summary, we distinguish gross profit and net profit as where gross profit only provides insight into the profitability of the primary business activities, and net profit gives an advanced view of a company’s financial health.
How to Calculate Gross Profit?
It's a straightforward method to calculate a business’s gross profit. It includes all sales revenue generated in a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year, throughout the primary business function of a company. Here, the cost of goods sold (COGS) is deducted from the sales revenue to find out the gross profit. Here's the equation for calculating gross profit:
- Gross Profit = Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
For Example, if a company’s total revenue from potential sales is $100,000 and its cost of goods sold (COGS) is $60000, then the gross profit would be $40000.
Components of Gross Profit

Revenue: The Total Income Generated From Sales
Revenue is an important component of gross profit that determines how well a business generates total income through sales by its primary business functions for a specific period. This revenue is the backbone of a business to sustain itself financially in the market and to turn it into a successful venture over time.
High revenue generation lets businesses dominate the market and potentially bring associated benefits like minimum employee turnover, market expansion, and minimized losses and exits. Thus, every business should focus on generating good revenue to lead a successful business.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS is the value associated with the manufacturing or production of goods that a business sells. This cost includes all relevant expenses of producing goods, such as fixed and variable costs.
This cost varies according to the output quantity. Plus, in the long term, businesses get cost reductions by mastering production. This is a paramount component in calculating the gross profit. Organizations should consider reducing the manufacturing cost of goods, which helps increase gross profit.
Understand Gross Profit Margin

Gross Profit Margin and Its Calculation
Gross profit margin is the financial metric that measures the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold (COGS). It indicates how a business generates profit relevant to the core business functions without adding other operational costs.
Gross profit margin is the percentage value of gross profit pertinent to the total sales revenue of a business's primary operations. It's calculated using the formula below:
- Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Sales Revenue) × 100%
An example of a detailed calculation figure is:
- Sales Revenue = $500,000
- COGS = $300,000
- Gross Profit = $500,000 - $300,000 equal to $200,000
- Gross Profit margin = ($200,000 / $500,000) × 100% that equal to 40%
Relationship Between Gross Profit Margin and Business Sustainability
Gross profit margin clearly indicates how strong the percentage of gross profit a business generates, pertaining to the total sales closed during a certain period. It's a clear financial matrix that showcases the profitability and long-term viability of a business.
The relationship between business sustainability and gross profit margin is positive. A good gross profit margin enhances business sustainability, while a low margin negatively affects it.
A healthy gross profit margin reflects effective cost management and adequate revenue generation for long-term viability. Conversely, a low margin indicates pricing or cost challenges, posing business sustainability risks.
Therefore, businesses should focus on implementing strategies to increase sales and minimize the cost of goods sold (COGS). This ensures a high percentage of gross profit margin.
Benchmarking Gross Profit Margin for Industry Comparison and Analysis
It's a valuable practice for businesses to benchmark gross profit margins for industry comparison and analysis. This is helpful to get useful insight into the company’s performance based on gross profit margin against industry peers.
Also, setting benchmarks helps businesses enhance the gross profit margin, which lets them achieve targets and discover their areas of strength and weakness. It also helps them make strategic decisions and survive in a competitive market.
Factors Affecting Gross Profit
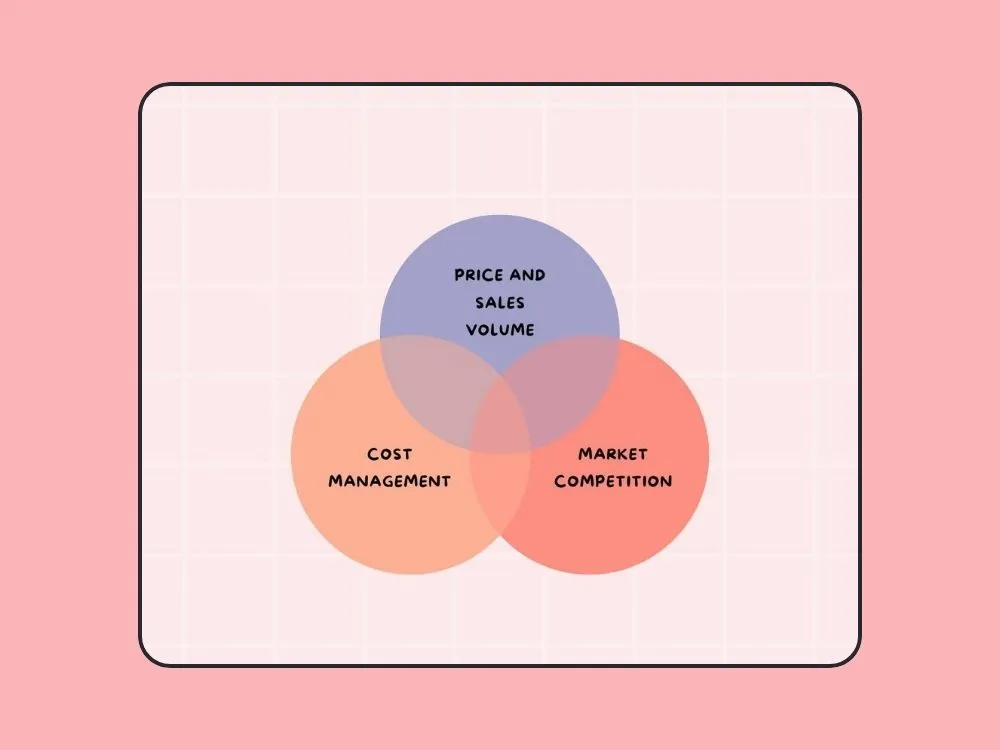
Price and Volume
Several factors impact the gross profit of a business, and one such factor is price and sales volume. A company’s total revenue is based on sales volume, where the product or service price is a direct influencing factor in determining the number of sales.
Without sufficient sales, there wouldn't be enough revenue, which may impact gross profit. In most cases, price and sales volume have a negative connection where goods with high price margins tend to move more slowly in sales, and low-priced goods move faster in sales.
On the other hand, even if the low-priced goods are sold in greater numbers, the total sales value would be minimal. Every business must set its product price optimally to get a moderate sales value that brings a good gross profit to the company.
Cost Management
Cost management of goods is another important factor that influences a company’s gross profit value. It's necessary to find out the best possible ways to control the COGS that can maximize the value of the gross profit of a business.
Firms follow various strategies to minimize the costs, such as reducing unnecessary production expenditures, minimizing inward returns of goods, and obtaining materials from quality vendors at low prices are some essential tips that significantly reduce the COGS and maximize the gross profit of a business.
Market Competition
Market competition is also a pivotal factor affecting gross profit, where generating adequate sales and revenue is highly competitive when the products are identical. Some large enterprises offer products at low sales prices because they can afford that price by having lower production costs.
To compete with these kinds of organizations, a business needs to strive hard and implement applicable strategies. Here, every startup faces this competition issue at the initial stage, which greatly impacts the gross profit.
In the long term, with appropriate strategies and building brand awareness and trust, businesses can break this competition and sustain in the market with an acceptable gross profit value.
Utilizing Gross Profit Data

Making Informed Business Decisions Based on Gross Profit Insights
Gross profit insights are a great source of financial indicators that can be effectively used to make informed business decisions. It also shows the profitability of an organization that comes from total sales revenue over a period and the cost of goods sold to generate the sales revenue.
By identifying gross profit, a business can utilize the necessary data insights to make future decisions and rectify the areas of weakness. This is helpful to drive a business to achieve its mission and protect it from unexpected losses.
Identifying Areas of Improvement and Implementing Strategies for Profit Maximization
The data insights derived from the gross profit of an organization explicitly indicate the necessary areas that the company should focus on to make improvements. This helps implement strategies for maximizing profit.
Identifying the lagging causes that directly impact the gross profit of a business is important. Factors like drops in sales revenue, increased production costs, excessive inward returns of sold goods, and many other factors can significantly affect the gross profit and eventually make an organization fail.
Therefore, it's crucial to rectify these drawbacks by identifying the root causes for decreased gross profit and implementing strategies to resolve them.
Communicating Gross Profit Information to Stakeholders and Investors
Stakeholders and investors are very keen to get information regarding the profitability of a business, and it helps them invest more and increase their involvement. It's necessary to communicate the gross profit information to the stakeholders and investors so that they find it useful to make decisions regarding their investments.
Moreover, it motivates them to introduce more investors to the business, and getting data insights is useful to them and makes them safe from losses. A cohesive decision-making process presents multiple benefits to a business. This is ensured by communicating necessary information with the concerned parties, like investors and stakeholders.
Common Pitfalls and Challenges
Potential Errors While Calculating and Interpreting Gross Profit
While calculating gross profit, there may be chances for potential errors. Organizations should be aware of these errors to avoid inaccurate calculations. Missing some of the production or manufacturing costs when calculating the COGS or missing sales data may result in an inaccurate calculation.
Also, taking operational costs into account causes errors because it's only taken into calculating the net profit of a business. A business should avoid errors in gross profit calculation. If not, it may mislead information, affect decision-making, and consequently lead to business losses.
Overlooking Other Financial Indicators by Solely Focusing on Gross Profit
This is a common pitfall where businesses can't solely rely on gross profit data to make informed business decisions. To make effective financial decisions, a business should focus on various financial metrics such as net profit, cash flow, operating expenses, ROI, and many more.
These metrics ensure a holistic approach to financial planning and decision-making. Gross profit is just an indicator that shows how well a business generates sales out of the goods sold, and it doesn’t completely state the financial status of a business. Therefore, companies should combine all necessary indicators to ensure a sustainable business approach.
Final Thoughts
Understanding gross profit is crucial for entrepreneurs striving to improve profitability and long-term sustainability in the market. Gross profit functions as a vital financial indicator for businesses that offer useful insights into profitability, cost control, pricing strategies, financial decision-making, and investor perceptions.
It's the difference between revenue from sales and the cost of goods sold (COGS). Businesses can calculate gross profit margin to measure their financial stability and industry performance while considering factors like price, volume, cost management, and market competition.
FAQs
Q1: What is gross profit, and why is it important?
Gross profit is sales revenue minus the cost of goods sold. It's crucial for entrepreneurs as it shows how much money a business makes from selling products or services, helping to measure profitability.
Q2: How is gross profit different from net profit?
Gross profit only considers sales and production costs, while net profit deducts all operating expenses and taxes. Gross profit shows core business profitability, while net profit gives overall financial health.
Q3: How do you calculate gross profit?
To find out gross profit, it is essential to subtract the cost of goods sold from total sales revenue.
Q4: How can businesses improve gross profit?
Businesses can enhance gross profit by optimizing pricing, reducing production costs, and managing inventory efficiently.
Q5: How do entrepreneurs use gross profit data for decisions?
Gross profit data helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions about pricing, inventory, and business growth.
Q6: Why is benchmarking gross profit important?
Benchmarking helps businesses compare their performance with industry peers and identify areas for improvement.
Explore Related Posts
https://smarttoolsai.com/post/multi-step-income-statement-a-practical-guide-for-financial-clarity
https://smarttoolsai.com/post/high-risk-merchant-account-at-highriskpay-com
.webp)