
What Is Supply Chain Management? Definition, Benefits, and Strategies
Have you ever thought about the process behind your favorite products showing up at your door? You simply click a button and your product appears a few days later. That's what efficient supply chain management does. When businesses get it right, customers stay happy and companies make more money. When they get it wrong, you end up refreshing tracking pages for days and questioning your life choices.
I've worked with businesses that ran smoothly and others that descended into chaos because their supply chain had zero strategy. Trust me, you don't want to be on the chaos side. So let's break down what supply chain management actually is and why it matters so much.
Key Takeaways
- Understand what supply chain management is and how it connects every step from supplier to customer.
- Learn the core components that make supply chains work smoothly.
- Discover proven strategies that increase efficiency and reduce costs.
- Explore supply chain software options for different business sizes.
- Avoid common mistakes that disrupt operations and hurt profitability.
What Is Supply Chain Management?
SCM is a whole process that allows products to get from point A (wherever they're made) to point B (your customer's hands) smoothly. It covers the journey of raw materials becoming products, stored in a warehouse, shipped out, and delivered to customers. It oversees each of these moving pieces functioning together.
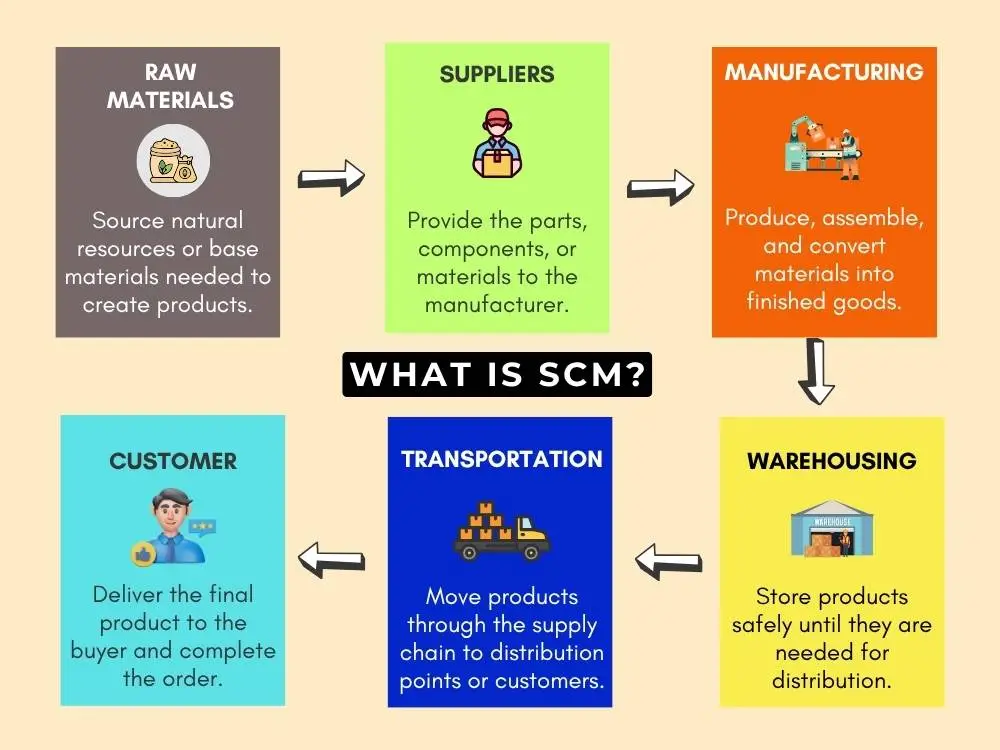
It includes suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and delivery trucks, each doing their job. If you have an SCM that works, customers will receive their orders on time, and the business won't waste time or money. If you don't? You'll receive the dreaded "shipping delayed" email, or the store will have empty shelves everywhere.
Why Supply Chain Management Matters
You might ask, Do companies really need to obsess over SCM? The answer is yes unless they enjoy losing money and angry customer emails. Here is why it matters.
- Lower Operating Costs: Good SCM cuts waste and reduces storage needs. This helps companies avoid unnecessary spending on operational expenses.
- Happier Customers: Fast and reliable delivery keeps customers loyal. After all, nobody cheers for late shipments.
- Better Collaboration: SCM encourages smooth communication between partners in the chain. Strong relationships lead to fewer mistakes.
- Stronger Competitive Advantage: Companies with great SCM beat slower competitors. You win over your rivals when you deliver faster and cheaper.
Many other reasons mandate the importance of SCM, which we'll see in the "Benefits" section.
Key Components of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management incorporates several components that work together. Let's take a closer look at what exactly is involved in bringing the whole system to life.
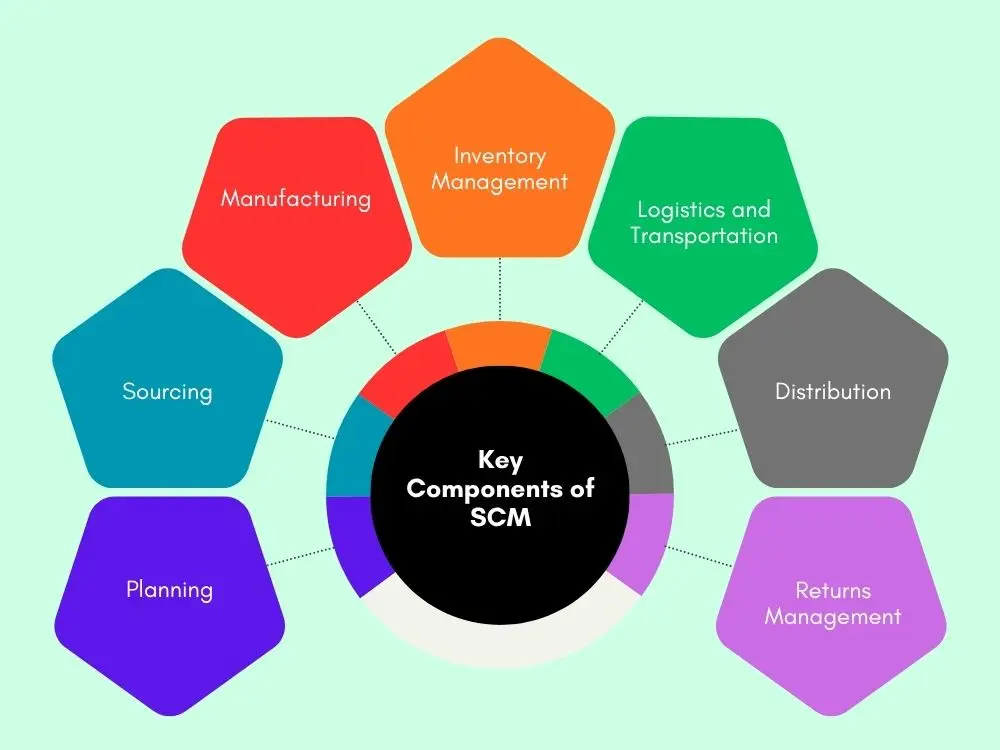
- Planning: This is the initial step in the entire process. What you actually do is future forecasting by learning customers' wants, knowing the price, and scheduling the time of events. It also includes having an alternative scheme for when hard times come.
- Sourcing: The focus here is to identify the most suitable suppliers and establish good working relationships with them. You aren't simply after the lowest price. They should supply quality products and, more importantly, shouldn't run away when problems arise.
- Manufacturing: A process that turns your raw materials into final products. You are overseeing the production, controlling the quality, and efficiency of workers and machines. If you fail to coordinate this properly, the whole operation downstream suffers. Also, check this guide on total manufacturing cost to get a comprehensive idea.
- Inventory Management: Receiving and counting the products in stock so that you are aware of what you have, where it is, when you will need more supplies, etc. Having too much stock means that money is tied up in inventory. Having fewer leads to customer disappointment.
- Logistics and Transportation: An essential function that enables products to be easily transported from one place to another without loss or damage. Logistics involves the storage of products, the selection of a shipping method, route planning, as well as customs handling if you export products.
- Distribution: Choosing the way the products get to the customers, whether through retailers, wholesalers, shipping directly to customers, or a combination of all. The distribution strategy can either enhance or destroy the customer experience.
- Returns Management: Also referred to as reverse logistics. During the return process of goods from customers, you must handle them in an organized way. This will help enhance brand reputation and customers' trust. Also, check this guide on return item chargeback to know more about returns and handling.
Key Benefits of Effective Supply Chain Management
Great SCM helps companies reap multiple benefits. Here are the good changes that you can notice:
- Better Efficiency: Effective SCM removes the unrealistic processes that create delays. Your operations will be smooth, and nothing will interfere with the transport of products. Plus, the products will be in your hands in no time.
- Higher Profitability: This is the major advantage. Lowering waste and getting products moving will result in an increase in your profit margins. You won't be losing money on express shipping or having unsold products in stock for so long.
- Improved Visibility: Modern supply chain tools show the current situation, not last week. This helps you easily track the product location, inventory status, and also detect problems before they turn into big issues.
- More Flexibility: The markets are rapidly changing. The consumers' needs may change instantly. When you have a solid supply chain, it lets you adapt without panicking. Plus, it helps pivot according to the sudden demand spikes and supplier issues.
- Stronger Supplier Relationships: Good, consistent communication and treating suppliers as partners will keep them positive about you. You will receive lower prices and quicker delivery. Plus, your orders will be prioritized even if there is a shortage of products.
- Happier Customers: Good delivery speed, correct orders, optimum quality, and simple returns help in customer retention. When SCM is properly done, you will have great and happy customers.
- Lower Risk: A properly managed supply chain doesn't put all the risk on one supplier or one route. If one thing goes wrong, your whole system doesn't get affected.
Supply Chain Management Strategies That Work
Let’s get right into the practical side of things. Below are strategies that are tried and tested, which aid companies in reinforcing their supply chain activities.
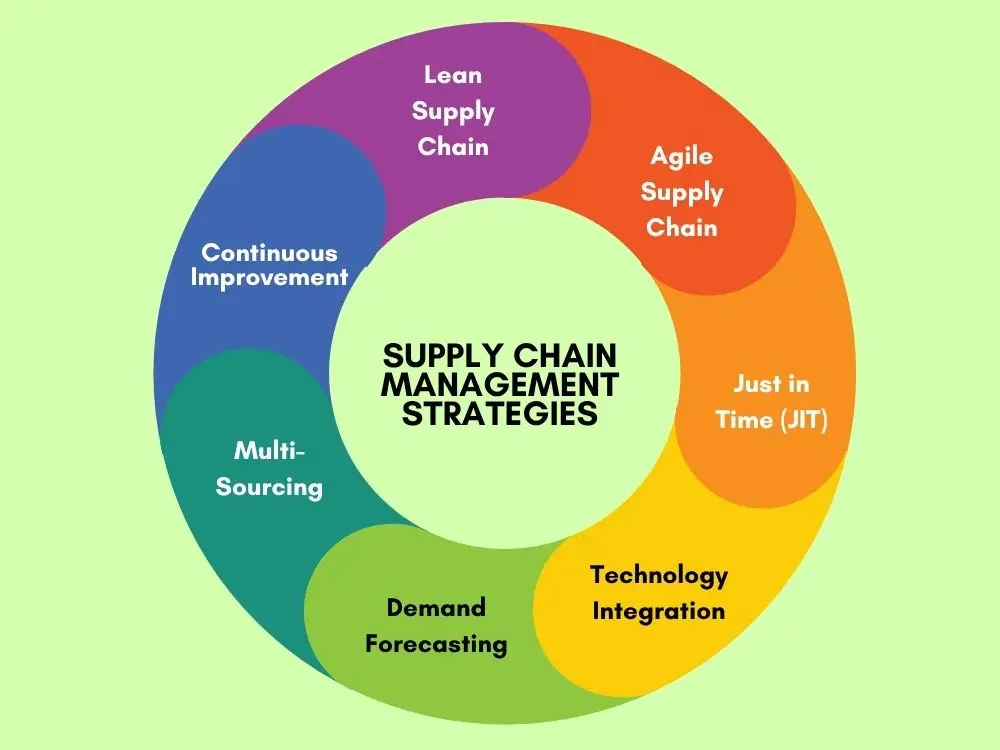
1. Lean Supply Chain
A lean approach focuses on waste reduction and flow improvement. The objective is to create more value with less input. This strategy is most effective in conditions where the demand is stable.
2. Agile Supply Chain
The agile supply chain is swift to respond to the changes in the market. It's relevant for industries like fashion or consumer electronics that move very fast.
3. Just in Time (JIT)
JIT minimizes the inventory costs by receiving goods only at the time of need. On the other hand, the risk of delays is the downside of this strategy, and thus it requires reliable suppliers.
4. Technology Integration
Modern supply chains adopt the following technologies:
- ERP systems for planning
- Automation tools for efficiency
- Inventory management software for stock accuracy
- Tracking tools for shipment visibility
With advanced technologies, companies acquire speed and accuracy.
5. Demand Forecasting
A strategy that uses historical data and market trends to forecast future demand. When done right, it helps prevent stockouts and overstocks. By the way, have you ever been in a store that couldn't keep a hot item in stock right before the holiday rush? This is an example of poor forecasting.
6. Multi-Sourcing
Instead of relying on a single supplier, companies select several suppliers. This not only decreases the risk but also prevents major shortages.
7. Continuous Improvement
Excellent supply chains never stay static. Companies evaluate their performance and implement minor changes regularly to maintain their efficiency.
The Role of Supply Chain Management Software
Technology can make a supply chain from messy to fine-tuned. A good software provides tracking in real time, supplier management, automated reporting, and predictive analytics to aid in identifying problems before they turn into obstacles.
These tools prevent errors and give you insights you'd never catch manually. Once you use SCM software, you won't go back to spreadsheets. Here's a breakdown of popular tools based on business size:
| For Small Businesses | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Software | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
| 1. Zoho Inventory |
|
|
|
| 2. inFlow Inventory |
|
|
|
| 3. Ordoro |
|
|
|
| For Mid-Sized Businesses | |||
| Fishbowl |
|
|
|
| Cin7 |
|
|
|
| TradeGecko (now QuickBooks Commerce) |
|
|
|
| For large Enterprises | |||
| SAP SCM |
|
|
|
| Oracle SCM Cloud |
|
|
|
| Blue Yonder (formerly JDA) |
|
|
|
Common Supply Chain Management Mistakes
Even experienced businesses mess up their supply chains. Here are some common mistakes that cause major headaches and how to avoid them.
- Poor Communication: This mistake can cause delays in the process. Suppliers, warehouses, customers, and teams need to be in good communication with each other to avoid this kind of issue.
- Ignoring Technology: Depending only on traditional spreadsheets to manage your supply chain is no longer a great choice. Have software tools that are capable of doing the entire process faster and smoothly.
- Weak Inventory Control: Bad inventory control leads to either waste or impacts prompt order fulfillment. That's why you must have a proper inventory management system.
- No Backup Plans: A problem with one supplier shouldn't affect your whole operation. Always have backup suppliers and alternative routes ready.
- Choosing the Cheapest Supplier: Low prices are tempting until you face other problems like delivery delays, quality issues, a bankrupt supplier, etc. Usually, the cheap option turns out to be more expensive eventually.
- Not Tracking Performance: If you don't monitor the performance of suppliers and processes, the bad ones will remain and you will lose good opportunities.
Tips for Building a Strong Supply Chain
Here are some useful tips you can implement immediately.
- Go for suppliers who are reliable and keep good communication.
- Frequently analyze data to understand trends and problems.
- Automate repetitive tasks to reduce unwanted errors.
- Invest in training so your team understands the system.
- Review performance metrics to measure progress.
- Be flexible as the market is always changing.
Wrapping Up
Supply chain management is important for many reasons. It fulfills the entire process from manufacturing to reaching customers. SCM brings many benefits to businesses, and you can improve it by applying key strategies like JIT, demand forecasting, agile supply chain, lean, etc. Plus, software tools play a key role in streamlining the process and reducing human errors.
FAQs
Q1: What's the difference between supply chain management and logistics?
Logistics only handles the part of the supply chain that deals with transportation and storage. However, SCM is the complete process from acquiring raw materials to delivering finished goods to customers.
Q5: How much does supply chain management software cost?
The price range is extensive, depending on the requirements you have. Solutions for small businesses begin at around $50-200 per month. The price of mid-sized tools varies from $500 to $2,000 monthly. The cost of enterprise systems can start from tens of thousands a month, plus the implementation fee.
.webp)